2V0-41.23 Exam Questions - Online Test
2V0-41.23 Premium VCE File

150 Lectures, 20 Hours
Exam Code: 2V0-41.23 (Practice Exam Latest Test Questions VCE PDF)
Exam Name: VMware NSX 4.x Professional
Certification Provider: VMware
Free Today! Guaranteed Training- Pass 2V0-41.23 Exam.
Also have 2V0-41.23 free dumps questions for you:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which troubleshooting step will resolve an error with code 1001 during the configuration of a time-based firewall rule?
- A. Reinstalling the NSX VIBs on the ESXi host.
- B. Restarting the NTPservice on the ESXi host.
- C. Changing the lime zone on the ESXi host.
- D. Reconfiguring the ESXI host with a local NTP server.
Answer: B
Explanation:
According to the web search results, error code 1001 is related to a time synchronization issue between the ESXi host and the NSX Manager. This can cause problems when configuring a time-based firewall rule, which requires the ESXi host and the NSX Manager to have the same time zone and NTP server settings . To resolve this error, you need to restart the NTP service on the ESXi host to synchronize the time with the NSX Manager. You can use the following command to restart the NTP service on the ESXi host:
/etc/init.d/ntpd restart
The other options are not valid solutions for this error. Reinstalling the NSX VIBs on the ESXi host will not fix the time synchronization issue. Changing the time zone on the ESXi host may cause more discrepancies with the NSX Manager. Reconfiguring the ESXi host with a local NTP server may not be compatible with the NSX Manager’s NTP server.
NEW QUESTION 2
An administrator is configuring service insertion for Network Introspection. Which two places can the Network Introspection be configured? (Choose two.)
- A. Host pNIC
- B. Partner SVM
- C. Tier-0 gateway
- D. Tier-1 gateway
- E. Edge Node
Answer: AB
Explanation:
Network Introspection is a service insertion feature that allows third-party network security services to
monitor and analyze the traffic between virtual machines. Network Introspection can be configured on the host pNIC or on the partner SVM, depending on the type of service and the deployment model. The host pNIC configuration is used for services that require traffic redirection from the physical network to the service virtual machine. The partner SVM configuration is used for services that require traffic redirection from the virtual network to the service virtual machine. Network Introspection cannot be configured on the Tier-0 or Tier-1 gateways, as they are not part of the data plane where the service insertion occurs. Network Introspection also cannot be configured on the edge node, as it is a logical construct that hosts the Tier-0 and Tier-1 gateways. References: Distributed Service Insertion, NSX Securing “Anywhere” Part IV
NEW QUESTION 3
Which TraceFlow traffic type should an NSX administrator use tor validating connectivity between App and DB virtual machines that reside on different segments?
- A. Multicast
- B. Unicast
- C. Anycast
- D. Broadcast
Answer: B
Explanation:
Unicast is the traffic type that an NSX administrator should use for validating connectivity between App and DB virtual machines that reside on different segments. According to the VMware documentation1, unicast traffic is the traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to one destination. Unicast traffic is the most common type of traffic in a network, and it is used for applications such as web browsing, email, file transfer, and so on2. To perform a traceflow with unicast traffic, the NSX administrator needs to specify the source and destination IP addresses, and optionally the protocol and related parameters1. The traceflow will show the path of the packet across the network and any observations or errors along the way3. The other options are incorrect because they are not suitable for validating connectivity between two specific virtual machines. Multicast traffic is the traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to multiple destinations simultaneously2. Multicast traffic is used for applications such as video streaming, online gaming and group communication4. To perform a traceflow with multicast traffic, the NSX administrator needs to specify the source IP address and the destination multicast IP address1. Broadcast traffic is the traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to all devices on the same subnet2. Broadcast traffic is used for applications such as ARP, DHCP, and network discovery. To perform a traceflow with broadcast traffic, the NSX administrator needs to specify the source IP address and the destination MAC address as FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF1. Anycast traffic is not a valid option, as it is not supported by NSX Traceflow. Anycast traffic is a traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to the nearest or best destination among a group of devices that share the same IP address. Anycast traffic is used for applications such as DNS, CDN, and load balancing.
NEW QUESTION 4
Where in the NSX UI would an administrator set the time attribute for a time-based Gateway Firewall rule?
- A. The option to set time-based rule is a clock Icon in the rule.
- B. The option to set time based rule is a field in the rule Itself.
- C. There Is no option in the NSX U
- D. It must be done via command line interface.
- E. The option to set time-based rule is a clock Icon in the policy.
Answer: D
Explanation:
According to the VMware documentation1, the clock icon appears on the firewall policy section that you want to have a time window. By clicking the clock icon, you can create or select a time window that applies to all the rules in that policy section. The other options are incorrect because they either do not exist or are not related to the time-based rule feature. There is no option to set a time-based rule in the rule itself, as it is a policy-level setting. There is also an option to set a time-based rule in the NSX UI, so it does not require using the command line interface.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.1/administration/GUID-8572496E-A60E-48C3-A016-4A081AC8
NEW QUESTION 5
Which three of the following describe the Border Gateway Routing Protocol (BGP) configuration on a Tier-0 Gateway? (Choose three.)
- A. Can be used as an Exterior Gateway Protocol.
- B. It supports a 4-byte autonomous system number.
- C. The network is divided into areas that are logical groups.
- D. EIGRP Is disabled by default.
- E. BGP is enabled by default.
Answer: ABD
Explanation:
* A. Can be used as an Exterior Gateway Protocol. This is correct. BGP is a protocol that can be used to exchange routing information between different autonomous systems (AS). An AS is a network or a group of networks under a single administrative control. BGP can be used as an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) to connect an AS to other ASes on the internet or other external networks1
* B. It supports a 4-byte autonomous system number. This is correct. BGP supports both 2-byte and 4-byte AS numbers. A 2-byte AS number can range from 1 to 65535, while a 4-byte AS number can range from 65536 to 4294967295. NSX supports both 2-byte and 4-byte AS numbers for BGP configuration on a Tier-0 Gateway2
* C. The network is divided into areas that are logical groups. This is incorrect. This statement describes OSPF, not BGP. OSPF is another routing protocol that operates within a single AS and divides the network into areas to reduce routing overhead and improve scalability. BGP does not use the concept of areas, but rather uses attributes, policies, and filters to control the routing decisions and traffic flow3
* D. FIGRP Is disabled by default. This is correct. FIGRP stands for Fast Interior Gateway Routing Protocol, which is an enhanced version of IGRP, an obsolete routing protocol developed by Cisco. FIGRP is not supported by NSX and is disabled by default on a Tier-0 Gateway.
* E. BGP is enabled by default. This is incorrect. BGP is not enabled by default on a Tier-0 Gateway. To enable BGP, you need to configure the local AS number and the BGP neighbors on the Tier-0 Gateway using the NSX Manager UI or API.
To learn more about BGP configuration on a Tier-0 Gateway in NSX, you can refer to the following resources: 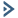 VMware NSX Documentation: Configure BGP 1
VMware NSX Documentation: Configure BGP 1 VMware NSX 4.x Professional: BGP Configuration
VMware NSX 4.x Professional: BGP Configuration  VMware NSX 4.x Professional: BGP Troubleshooting
VMware NSX 4.x Professional: BGP Troubleshooting
NEW QUESTION 6
Which two of the following will be used for Ingress traffic on the Edge node supporting a Single Tier topology? (Choose two.)
- A. Inter-Tier interface on the Tier-0 gateway
- B. Tier-0 Uplink interface
- C. Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR
- D. Tier-1 SR Router Port
- E. Downlink Interface for the Tier-1 DR
Answer: BC
Explanation:
The two interfaces that will be used for ingress traffic on the Edge node supporting a Single Tier topology are: B. Tier-0 Uplink interface
B. Tier-0 Uplink interface C. Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR
C. Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR
The Tier-0 Uplink interface is the interface that connects the Tier-0 gateway to the external network. It is used to receive traffic from the physical router or switch that is the next hop for the Tier-0 gateway. The Tier-0 Uplink interface can be configured with a static IP address or use BGP to exchange routes with the external network.
The Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR is the interface that connects the Tier-0 gateway to the workload segments. It is used to receive traffic from the VMs or containers that are attached to the segments. The Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR is a logical interface (LIF) that is distributed across all transport nodes that host the segments. The Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR has an IP address that acts as the default gateway for the VMs or containers on the segments.
NEW QUESTION 7
What are two valid options when configuring the scope of a distributed firewall rule? (Choose two.)
- A. DFW
- B. Tier-1 Gateway
- C. Segment
- D. Segment Port
- E. Group
Answer: CE
Explanation:
* C. Segment. This is correct. A segment is a logical construct that represents a layer 2 broadcast domain and a layer 3 subnet in NSX. A segment can be used to group and connect virtual machines, containers, or bare metal hosts that belong to the same application or service. A segment can also be used as the scope of a distributed firewall rule, which means that the rule will apply to all the traffic that enters or exits the segment12
* E. Group. This is correct. A group is a logical construct that represents a collection of objects in NSX, such as segments, segment ports, virtual machines, IP addresses, MAC addresses, tags, or security policies. A group can be used to define dynamic membership criteria based on various attributes or filters. A group can also be used as the scope of a distributed firewall rule, which means that the rule will apply to all the traffic that matches the group membership criteria32
NEW QUESTION 8
Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator configured NSX Advanced Load Balancer to load balance the production web server traffic, but the end users are unable to access the production website by using the VIP address.
Which of the following Tier-1 gateway route advertisement settings needs to be enabled to resolve the problem? Mark the correct answer by clicking on the image.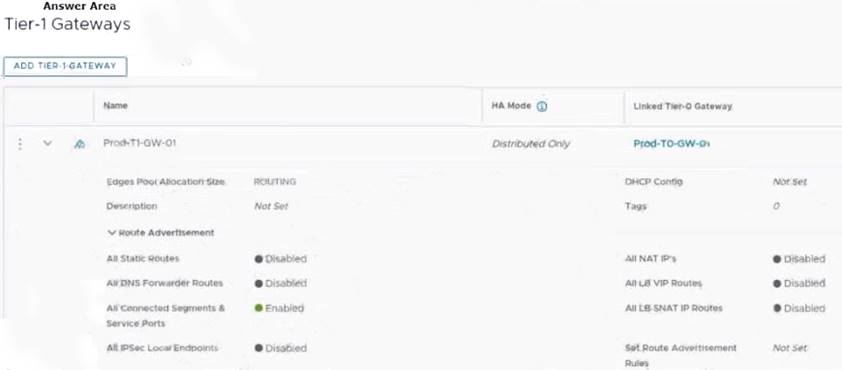
Solution:
The correct answer is to enable the option All LB VIP Routes on the Tier-1 gateway route advertisement settings. This option allows the Tier-1 gateway to advertise the NSX Advanced Load Balancer LB VIP routes to the Tier-0 gateway and other peer routers, so that the end users can reach the production website by using the VIP address1. The other options are not relevant for this scenario.
To mark the correct answer by clicking on the image, you can click on the toggle switch next to All LB VIP Routes to turn it on. The switch should change from gray to blue, indicating that the option is enabled. See the image below for reference:
Does this meet the goal?
- A. Yes
- B. Not Mastered
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 9
Which two built-in VMware tools will help Identify the cause of packet loss on VLAN Segments? (Choose two.)
- A. Flow Monitoring
- B. Packet Capture
- C. Live Flow
- D. Activity Monitoring
- E. Traceflow
Answer: BE
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation1, Packet Capture and Traceflow are two built-in VMware tools that can help identify the cause of packet loss on VLAN segments.
Packet Capture allows you to capture packets on a specific interface or segment and analyze them using tools such as Wireshark or tcpdump. Packet Capture can help you diagnose network issues such as misconfigured MTU, incorrect VLAN tags, or firewall drops.
Traceflow allows you to inject synthetic packets into the network and trace their path from source to destination. Traceflow can help you verify connectivity, routing, and firewall rules between virtual machines or segments. Traceflow can also show you where packets are dropped or modified along the way.
NEW QUESTION 10
When configuring OSPF on a Tler-0 Gateway, which three of the following must match in order to establish a neighbor relationship with an upstream router? (Choose three.)
- A. Naming convention
- B. MTU of the Uplink
- C. Subnet mask
- D. Address of the neighbor
- E. Protocol and Port
- F. Area ID
Answer: BCF
Explanation:
ccording to the VMware NSX Documentation, these are the three parameters that must match in order to establish an OSPF neighbor relationship with an upstream router on a tier-0 gateway: MTU of the Uplink: The maximum transmission unit (MTU) of the uplink interface must match the MTU of the upstream router interface. Otherwise, OSPF packets may be fragmented or dropped, causing neighbor adjacency issues.
MTU of the Uplink: The maximum transmission unit (MTU) of the uplink interface must match the MTU of the upstream router interface. Otherwise, OSPF packets may be fragmented or dropped, causing neighbor adjacency issues. Subnet mask: The subnet mask of the uplink interface must match the subnet mask of the upstream router interface. Otherwise, OSPF packets may not reach the correct destination or be rejected by the upstream router.
Subnet mask: The subnet mask of the uplink interface must match the subnet mask of the upstream router interface. Otherwise, OSPF packets may not reach the correct destination or be rejected by the upstream router. Area ID: The area ID of the uplink interface must match the area ID of the upstream router interface.
Area ID: The area ID of the uplink interface must match the area ID of the upstream router interface.
Otherwise, OSPF packets may be ignored or discarded by the upstream router.
NEW QUESTION 11
A company Is deploying NSX micro-segmentation in their vSphere environment to secure a simple application composed of web. app, and database tiers.
The naming convention will be:
• WKS-WEB-SRV-XXX
• WKY-APP-SRR-XXX
• WKI-DB-SRR-XXX
What is the optimal way to group them to enforce security policies from NSX?
- A. Use Edge as a firewall between tiers.
- B. Do a service insertion to accomplish the task.
- C. Group all by means of tags membership.
- D. Create an Ethernet based security policy.
Answer: C
Explanation:
The answer is C. Group all by means of tags membership.
Tags are metadata that can be applied to physical servers, virtual machines, logical ports, and logical segments in NSX. Tags can be used for dynamic security group membership, which allows for granular and flexible enforcement of security policies based on various criteria1
In the scenario, the company is deploying NSX micro-segmentation to secure a simple application composed of web, app, and database tiers. The naming convention will be: WKS-WEB-SRV-XXX
WKS-WEB-SRV-XXX  WKY-APP-SRR-XXX
WKY-APP-SRR-XXX  WKI-DB-SRR-XXX
WKI-DB-SRR-XXX
The optimal way to group them to enforce security policies from NSX is to use tags membership. For example, the company can create three tags: Web, App, and DB, and assign them to the corresponding VMs based on their names. Then, the company can create three security groups: Web-SG, App-SG, and DB-SG, and use the tags as the membership criteria. Finally, the company can create and apply security policies to the security groups based on the desired rules and actions2
Using tags membership has several advantages over the other options: It is more scalable and dynamic than using Edge as a firewall between tiers. Edge firewall is a centralized solution that can create bottlenecks and performance issues when handling large amounts of traffic3
It is more scalable and dynamic than using Edge as a firewall between tiers. Edge firewall is a centralized solution that can create bottlenecks and performance issues when handling large amounts of traffic3 It is more simple and efficient than doing a service insertion to accomplish the task. Service insertion is a feature that allows for integrating third-party services with NSX, such as antivirus or intrusion prevention systems. Service insertion is not necessary for basic micro-segmentation and can introduce additional complexity and overhead.
It is more simple and efficient than doing a service insertion to accomplish the task. Service insertion is a feature that allows for integrating third-party services with NSX, such as antivirus or intrusion prevention systems. Service insertion is not necessary for basic micro-segmentation and can introduce additional complexity and overhead. It is more flexible and granular than creating an Ethernet based security policy. Ethernet based security policy is a type of policy that uses MAC addresses as the source or destination criteria. Ethernet based security policy is limited by the scope of layer 2 domains and does not support logical constructs such as segments or groups.
It is more flexible and granular than creating an Ethernet based security policy. Ethernet based security policy is a type of policy that uses MAC addresses as the source or destination criteria. Ethernet based security policy is limited by the scope of layer 2 domains and does not support logical constructs such as segments or groups.
To learn more about tags membership and how to use it for micro-segmentation in NSX, you can refer to the following resources: VMware NSX Documentation: Security Tag 1
VMware NSX Documentation: Security Tag 1 VMware NSX Micro-segmentation Day 1: Chapter 4 - Security Policy Design 2
VMware NSX Micro-segmentation Day 1: Chapter 4 - Security Policy Design 2  VMware NSX 4.x Professional: Security Groups
VMware NSX 4.x Professional: Security Groups VMware NSX 4.x Professional: Security Policies
VMware NSX 4.x Professional: Security Policies
NEW QUESTION 12
Where is the insertion point for East-West network introspection?
- A. Tier-0 router
- B. Partner SVM
- C. Guest VM vNIC
- D. Host Physical NIC
Answer: C
Explanation:
The insertion point for East-West network introspection is the Guest VM vNIC. Network introspection is a service insertion feature that allows third-party network services to be integrated with NSX. Network introspection enables traffic redirection from the Guest VM vNIC to a service virtual machine (SVM) that runs the partner service. The SVM can then inspect, monitor, or modify the traffic before sending it back to the original destination1. The other options are incorrect because they are not the insertion points for East-West network introspection. The Tier-0 router is used for North-South routing and network services. The partner SVM is the service virtual machine that runs the partner service, not the insertion point. The host physical NIC is not involved in network introspection. References: Network Introspection Settings
NEW QUESTION 13
Which CLI command would an administrator use to allow syslog on an ESXi transport node when using the esxcli utility?
- A. esxcli network firewall ruleset set -r syslog -e true
- B. esxcli network firewall ruleset -e syslog
- C. esxcli network firewall ruleset set -r syslog -e false
- D. esxcli network firewall ruleset set -a -e false
Answer: A
Explanation:
To allow syslog on an ESXi transport node, the administrator needs to use the esxcli utility to enable the syslog ruleset in the ESXi firewall. The correct syntax for this command is esxcli network firewall ruleset set
-r syslog -e true, where -r specifies the ruleset name and -e specifies whether to enable or disable it. The options are incorrect because they either use an invalid syntax, such as omitting the ruleset name or
using -a instead of -r, or they disable the syslog ruleset instead of enabling it, which is the opposite of what
question asks. References: [ESXi Firewall Command-Line Interface], [Configure Syslog on ESXi Hosts]
NEW QUESTION 14
An NSX administrator is using ping to check connectivity between VM1 running on ESXi1 to VM2 running on ESXi2. The ping tests fails. The administrator knows the maximum transmission unit size on the physical switch is 1600.
Which command does the administrator use to check the VMware kernel ports for tunnel end point communication?
- A. esxcli network diag ping -I vmk0O -H <destination IP address>
- B. vmkping ++netstack=geneve -d -s 1572 <destination IP address>
- C. esxcli network diag ping -H <destination IP address>
- D. vmkping ++netstack=vxlan -d -s 1572 <destination IP address>
Answer: B
Explanation:
The command vmkping ++netstack=geneve -d -s 1572 <destination IP address> is used to check the VMwar kernel ports for tunnel end point communication. This command uses the geneve netstack, which is the default netstack for NSX-T. The -d option sets the DF (Don’t Fragment) bit in the IP header, which prevents the packet from being fragmented by intermediate routers. The -s 1572 option sets the packet size to 1572 bytes, which is the maximum payload size for a geneve encapsulated packet with an MTU of 1600 bytes.
The <destination IP address> is the IP address of the remote ESXi host or VM. References: : VMware NS Data Center Installation Guide, page 19. : VMware Knowledge Base: Testing MTU with the vmkping command (1003728). : VMware NSX-T Data Center Administration Guide, page 102.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which CLI command is used for packet capture on the ESXi Node?
- A. tcpdump
- B. debug
- C. pktcap-uw
- D. set capture
Answer: C
Explanation:
According to the VMware Knowledge Base, this CLI command is used for packet capture on the ESXi node. pktcap-uw stands for Packet Capture User World and is a tool that allows you to capture packets from various points in the network stack of an ESXi host. You can use this tool to troubleshoot network issues or analyze traffic flows.
The other options are either incorrect or not available for this task. tcpdump is not a valid CLI command for packet capture on the ESXi node, as it is a tool that runs on Linux systems, not on ESXi hosts. debug is not a valid CLI command for packet capture on the ESXi node, as it is a generic term that describes the process of finding and fixing errors, not a specific tool or command. set capture is not a valid CLI command for packet capture on the ESXi node, as it does not exist in the ESXi CLI.
NEW QUESTION 16
Match the NSX Intelligence recommendations with their correct purpose.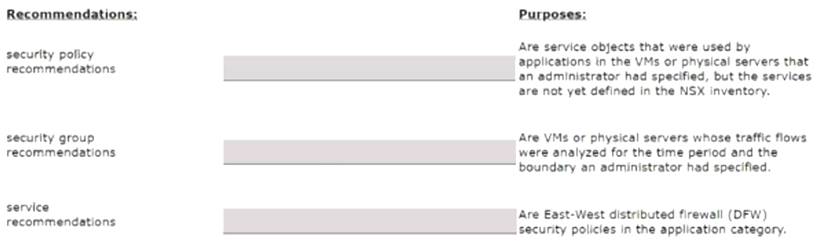
Solution:
 Security policy recommendations: Are East-West distributed firewall (DFW) security policies in the application category12.
Security policy recommendations: Are East-West distributed firewall (DFW) security policies in the application category12. Security group recommendations: Are VMs or physical servers whose traffic flows were analyzed for the time period and the boundary you had specified12.
Security group recommendations: Are VMs or physical servers whose traffic flows were analyzed for the time period and the boundary you had specified12. Service recommendations: Are service objects that were used by applications in the VMs or physical servers that you had specified, but the services are not yet defined in the NSX inventory12.
Service recommendations: Are service objects that were used by applications in the VMs or physical servers that you had specified, but the services are not yet defined in the NSX inventory12.Does this meet the goal?
- A. Yes
- B. Not Mastered
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 17
Which of the following settings must be configured in an NSX environment before enabling stateful active-active SNAT?
- A. Tier-1 gateway in active-standby mode
- B. Tier-1 gateway in distributed only mode
- C. An Interface Group for the NSX Edge uplinks
- D. A Punting Traffic Group for the NSX Edge uplinks
Answer: C
Explanation:
To enable stateful active-active SNAT on a Tier-0 or Tier-1 gateway, you must configure an Interface Group for the NSX Edge uplinks. An Interface Group is a logical grouping of NSX Edge interfaces that belong to the same failure domain. A failure domain is a set of NSX Edge nodes that share the same physical network infrastructure and are subject to the same network failures. By configuring an Interface Group, you can ensure that the stateful services are distributed across different failure domains and can recover from network failures1
NEW QUESTION 18
An administrator wants to validate the BGP connection status between the Tier-O Gateway and the upstream physical router.
What sequence of commands could be used to check this status on NSX Edge node?
- A. set vrf <ID>show logical-routers show <LR-D> bgp
- B. show logical-routers get vrfshow ip route bgp
- C. get gateways vrf <number>get bgp neighbor
- D. enable <LR-D> get vrf <ID>show bgp neighbor
Answer: C
Explanation:
The sequence of commands that could be used to check the BGP connection status between the Tier-O Gateway and the upstream physical router on NSX Edge node is get gateways, vrf <number>, get bgp neighbor. These commands can be executed on the NSX Edge node CLI after logging in as admin6. The firs command, get gateways, displays the list of logical routers (gateways) configured on the Edge node, along with their IDs and VRF numbers7. The second command, vrf <number>, switches to the VRF context of the desired Tier-O Gateway, where <number> is the VRF number obtained from the previous command7. The third command, get bgp neighbor, displays the BGP neighbor summary for the selected VRF, including the neighbor IP address, AS number, state, uptime, and prefixes received8. The other options are incorrect because they either use invalid or incomplete commands or do not switch to the correct VRF
context. References: NSX-T Command-Line Interface Reference, NSX Edge Node CLI Commands, Troubleshooting BGP on NSX-T Edge Nodes
NEW QUESTION 19
Which three data collection sources are used by NSX Network Detection and Response to create correlations/Intrusion campaigns? (Choose three.)
- A. Files and anti-malware (lie events from the NSX Edge nodes and the Security Analyzer
- B. East-West anti-malware events from the ESXi hosts
- C. Distributed Firewall flow data from the ESXi hosts
- D. IDS/IPS events from the ESXi hosts and NSX Edge nodes
- E. Suspicious Traffic Detection events from NSX Intelligence
Answer: ADE
Explanation:
The correct answers are A. Files and anti-malware (file) events from the NSX Edge nodes and the Security Analyzer, D. IDS/IPS events from the ESXi hosts and NSX Edge nodes, and E. Suspicious Traffic Detection events from NSX Intelligence. According to the VMware NSX Documentation3, these are the three data collection sources that are used by NSX Network Detection and Response to create correlations/intrusion campaigns.
The other options are incorrect or not supported by NSX Network Detection and Response. East-West anti-malware events from the ESXi hosts are not collected by NSX Network Detection and
Response3. Distributed Firewall flow data from the ESXi hosts are not used for correlation/intrusion
campaigns by NSX Network Detection and Response3.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/administration/GUID-14BBE50D-9931-4719-8F
NEW QUESTION 20
Refer to the exhibit.
Which two items must be configured to enable OSPF for the Tler-0 Gateway in the Image? Mark your answers by clicking twice on the image.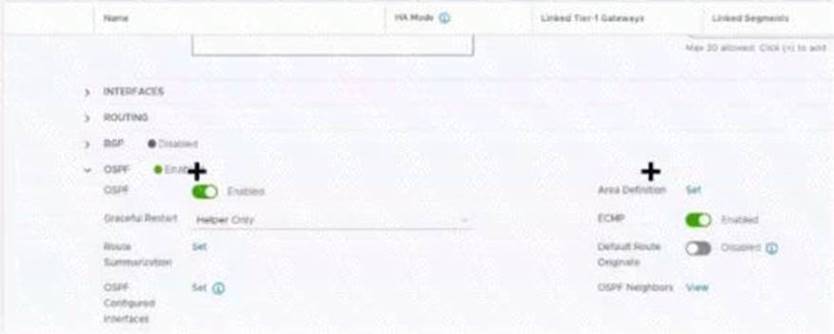
Solution:
The correct answer is to enable the OSPF toggle and to add an Area Definition for the Tier-0 gateway in image. These two items are required to configure OSPF on the Tier-0 gateway, as explained in the web search results123.
To mark your answers by clicking twice on the image, you can double-click on the toggle switch next
to OSPF to turn it on. The switch should change from gray to blue, indicating that the option is enabled. The you can double-click on the Set button next to Area Definition to add an area definition. A pop-up windo should appear where you can specify the area ID and type.
* 1. Click the OSPF toggle to enable OSPF 2. In the Area Definition field, click Set to add an area definition https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/administration/GUID-5BEC626C-5312-467D-B
Does this meet the goal?
- A. Yes
- B. Not Mastered
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 21
......
P.S. Dumps-hub.com now are offering 100% pass ensure 2V0-41.23 dumps! All 2V0-41.23 exam questions have been updated with correct answers: https://www.dumps-hub.com/2V0-41.23-dumps.html (106 New Questions)
- How Many Questions Of 3V0-42.20 Test Engine
- The Renewal Guide To 2V0-41.20 Test Engine
- 10 Tips For Rebirth 2VB-602 braindumps
- VMware 2V0-731 Dumps Questions 2021
- Update VMware 2V0-602 practice test
- All About Accurate 2VB-602 braindumps
- 10 Tips For Rebirth VCP550 dumps
- Most Recent 2V0-21.19 Bundle 2021
- High value VMware 2V0-602 exam
- 10 Tips For Improved VCP550 exam dumps


