1Z0-821 Exam Questions - Online Test
1Z0-821 Premium VCE File

150 Lectures, 20 Hours
Exam Code: 1Z0-821 (Practice Exam Latest Test Questions VCE PDF)
Exam Name: Oracle Solaris 11 System Administrator
Certification Provider: Oracle
Free Today! Guaranteed Training- Pass 1Z0-821 Exam.
Free demo questions for Oracle 1Z0-821 Exam Dumps Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which two options are characteristics of a fast reboot?
- A. A fast reboot bypasses grub.
- B. A fast reboot cannot be used after a system panic on the x86 platform.
- C. A fast reboot can only be executed on the SPARC platform when the config/fastreboot_default property for the svc:/system/boot-config:default service is set to true.
- D. A fast reboot uses an in-kernel boot loader to load the kernel into memory.
- E. A fast reboot is the default on all platforms.
Answer: CD
Explanation:
C: To change the default behavior of the Fast Reboot feature on the SPARC platform, so that a fast reboot is automatically performed when the system reboots, see below.
The following example shows how to set the property's value to true on the SPARC platform, so that a fast reboot is initiated by default:
# svccfg -s "system/boot-config:default" setprop config/fastreboot_default=true
# svcadm refresh svc:/system/boot-config:default
D: Fast Reboot implements an in-kernel boot loader that loads the kernel into memory and then switches to that kernel.
The firmware and boot loader processes are bypassed, which enables the system to reboot within seconds.
The Fast Reboot feature is managed by SMF and implemented through a boot configuration service, svc:/system/boot-config. The boot-config service provides a means for setting or changing the default boot configuration parameters. When the config/fastreboot_default property is set to true, the system performs a fast reboot automatically, without the need to use the reboot -f command. This property's value is set to true on the x86 platform. For task-related information, including how to change the default behavior of Fast Reboot on the SPARC platform, see Accelerating the Reboot Process on an x86 Based System.
Note: One new feature, called Fast Reboot, will allow the system to boot up without doing the routine set of hardware checks, a move that can make system boot times up to two- and-a-half times faster, Oracle claimed. This feature can be handy in that an administrator applying a patch or software update across thousands of Solaris deployments can reboot them all the more quickly.
NEW QUESTION 2
You create a flash archive of the Solaris 10 global zone on the serves named sysA. The archive name is s10-system.flar, and it is stored on a remote server named backup_server.
On sysA, you create a Solaris 10 branded zone named s10-zone.
You want to use the flash archive, located On" /net/bactup_servers/10-system.flar, to install the Operating system in the s10-zone zone.
Which command do you choose to install the s10-system.flar archive in the Solaris 10 branded zone (s10-zone)?
- A. zoneadm -z s10 -zone install - a /net/backup_server/s10-system.flar -u
- B. zonecfg -z s10 -zone install - a /net/backup_server/s10-system.flar -u
- C. zoneadm - z s10 -zone clone - s /net/backup_server/s10-system.flar
- D. zone cfg - a s10-zone create - t SUNWsolaris10\</net/backup_server/s10-system.flar
- E. zonecfg -z s10-zone install -f /net/backup/backup_server/s10-system.flar
Answer: A
Explanation:
The zoneadm command is the primary tool used to install and administer non-global zones. Operations using the zoneadm command must be run from the global zone on the target system.
How to Install the solaris10 Branded Zone
A configured solaris10 branded zone is installed by using the zoneadm command with the install subcommand.
Example: global# zoneadm -z s10-zone install -a /net/machine_name/s10-system.flar –u
NEW QUESTION 3
Select two statements that correctly describe the capabilities of the Distribution Constructor.
- A. ISO images for use with the Automated Installer (AI) can be created.
- B. Bootable USB images can be created for SPARC and x86 architectures.
- C. A single installation server can be used to create ISO images for SPARC and x86 architectures.
- D. Checkpoints can be used to pause the build, allowing scripts to run that modify theresulting ISO Image.
- E. A single Installation server can be used to create ISO images for Solaris 10 and Solaris11 operating systems.
Answer: AD
Explanation:
A: You can use the distribution constructor to create the following types of Oracle Solaris images:
* (A) x86 or SPARC ISO Image for Automated Installations
* Oracle Solaris x86 live CD image
* x86 or SPARC Oracle Solaris text installer image
* x86 Oracle Solaris Virtual Machine
Note: You can use the distribution constructor to build custom Oracle Solaris images. Then, you can use the images to install the Oracle Solaris software on individual systems or multiple systems. You can, also, use the distribution constructor to create Virtual Machine (VM) images that run the Oracle Solaris operating system.
D: Checkpointing Options
You can use the options provided in the distro_const command to stop and restart the build process at various stages in the image-generation process, in order to check and debug the image that is being built. This process of stopping and restarting during the build process is called checkpointing.
NEW QUESTION 4
The ZFS configuration on your server is:
Pool1 6.67G31K/pool Pool1/data31K31K/data
Select the three commands that you would use to 1. Create, 2. List, and 3. Delete a snapshot of the /data file system.
- A. zfs snapshot pool1/data@now
- B. zfs create snapshot pool1/data@now
- C. zfs list -t snapshot
- D. zfs list -t snapshot pool1/data
- E. zfs destroy pool1/data@now
- F. zfs destroy snapshot pool1/data@now
Answer: ADE
Explanation:
A: Snapshots are created by using the zfs snapshot command, which takes as its only argument the name of the snapshot to create.
D: You can list snapshots as follows:
# zfs list -t snapshot
E: Snapshots are destroyed by using the zfs destroy command. For example:
# zfs destroy tank/home/ahrens@now
NEW QUESTION 5
Oracle Solaris 11 kernel encounters a fatal error, and it results in a system panic.
What type of file does this generate?
- A. a.out
- B. objdump
- C. core dump
- D. tape dump
- E. crash dump
Answer: C
Explanation:
A kernel panic is a type of error that occurs when the core (kernel) of an operating system receives an instruction in an unexpected format or when it fails to handle properly. A kernel panic can also follow when the operating system can’t recover from a different type of error. A kernel panic can be caused by damaged or incompatible software or, more rarely, damaged or incompatible hardware.
When a server kernel panics it abruptly halts all normal system operations. Usually, a kernel process named panic() outputs an error message to the console and stores debugging information in nonvolitile memory to be written to a crash log file upon restarting the computer. Saving the memory contents of the core and associated debugging information is called a “core dump.”
NEW QUESTION 6
The line
set noexec_user_stack= l
should be added to the /etc/system file to prevent an executable stack while executing user programs. What is the purpose of this?
- A. help prevent core dumps on program errors
- B. help programs to execute more quickly by keeping to their own memory space
- C. log any messages into the stack log
- D. help make buffer-overflow attacks more difficult
Answer: D
Explanation:
How to Disable Programs From Using Executable Stacks Purpose: Prevent executable stack from overflowing. You must be in the root role.
Edit the /etc/system file, and add the following line: set noexec_user_stack=1
Reboot the system.
# reboot
NEW QUESTION 7
You are asked to troubleshoot networking issues on an unfamiliar system. Select the correct command to display what network devices are installed.
- A. ifconfig -a
- B. dladm show-dev
- C. dladm show-phys
- D. dladm show-ether
- E. netadm show-dev
- F. netadm show-ether
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 8
To confirm the IP address and netmask have been correctly configured on the network interfaces which command should you use?
- A. ipdilm show-if
- B. ipadm show-nic
- C. ipadm show-addr
- D. ipadm show-ifconfig
- E. ipadm show-addripadm show-mask
Answer: C
Explanation:
Show address information, either for the given addrobj or all the address objects configured on the specified interface, including the address objects that are only in the persistent configuration.
State can be: disabled, down, duplicate, inaccessible, ok, tentative Example:
# ipadm show-addr
ADDROBJ TYPE STATE ADDR
lo0/v4 static ok 127.0.0.1/8 lo0/v6 static ok ::1/128
NEW QUESTION 9
Select the packet type that identifies members of the group and sends information to all the network interfaces in that group.
- A. Unicast
- B. Multicast
- C. Broadcast
- D. Bayesian
- E. Quality of Service Priority
Answer: B
Explanation:
IPv6 defines three address types: unicast
Identifies an interface of an individual node.
multicast
Identifies a group of interfaces, usually on different nodes. Packets that are sent to the multicast address go to all members of the multicast group.
anycast
Identifies a group of interfaces, usually on different nodes. Packets that are sent to the anycast address go to the anycast group member node that is physically closest to the sender.
NEW QUESTION 10
You wish to troubleshoot some issues that you are having on the system. You want to monitor the /var/adm/messages file in real time. Which command would you use to do this?
- A. head
- B. tail
- C. cat
- D. file
- E. test
Answer: B
Explanation:
tail is a program on Unix and Unix-like systems used to display the last few lines of a text file or piped data.
By default, tail will print the last 10 lines of its input to the standard output. With command line options the number of lines printed and the printing units (lines, blocks or bytes) may be changed. The following example shows the last 20 lines of filename:
tail -n 20 filename
NEW QUESTION 11
You have set up the task.max-lwps resource control on your Solaris 11 system.
Which option describes how to configure the system so that syslogd notifies you when the resources control threshold value for the task.max-lwps resource has been exceeded?
- A. Use the rctladm command to enable the global action on the task.max-lwpa resource control.
- B. Modify the /etc/syslog.conf file to activate system logging of all violations of task.max- lwps and then refresh then svc: /system/system-log:default service.
- C. Activate system logging of all violations of task.max-lwpp in the /etc/rctldm.conf file and then execute the rctladm-u command.
- D. Use the prct1 command to set the logging of all resource control violations at the time the task.max-lwps resource control is being setup.
- E. Use the setrct1 command to set the logging of all resource control violations for the task.max-lwps resource control.
Answer: A
Explanation:
rctladm - display and/or modify global state of system resource controls
The following command activates system logging of all violations of task.max-lwps.
# rctladm -e syslog task.max-lwps
#
NEW QUESTION 12
Which network protocol provides connectionless, packet-oriented communication between applications?
- A. TCP
- B. UDP
- C. IP
- D. ICMP
- E. NFS
- F. IPSec
Answer: B
Explanation:
The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is one of the core members of the Internet Protocol Suite, the set of network protocols used for the Internet. With UDP, computer applications can send messages, in this case referred to as datagrams, to other hosts on an Internet Protocol (IP) network without requiring prior communications to set up special transmission channels or data paths.
Compared to TCP, UDP is a simpler message-based connectionless protocol.
NEW QUESTION 13
Subnets are created by using .
- A. subnet
- B. netmask
- C. unicast
- D. broadcast
Answer: B
Explanation:
The process of subnetting involves the separation of the network and subnet portion of an address from the host identifier. This is performed by a bitwise AND operation between the IP address and the (sub)network prefix. The result yields the network address or prefix, and the remainder is the host identifier.
The routing prefix of an address is written in a form identical to that of the address itself. This is called the network mask, or netmask, of the address. For example, a specification of the most-significant 18 bits of an IPv4 address, 11111111.11111111.11000000.00000000, is written as 255.255.192.0.
NEW QUESTION 14
Identify three differences between the shutdown and init commands.
- A. Only shutdown broadcasts a final shutdown warning to all logged-in users.
- B. init does not terminate all services normall
- C. The shutdown command performs a cleaner shutdown of all services.
- D. The shutdown command can only bring the system to the single-user mileston
- E. The init command must be used to shut the system down to run level 0.
- F. Only shutdown sends a shutdown message to any systems that are mounting resources from the system that is being shut down.
- G. The shutdown command will shut the system down and turn off power; init will only shut the system down.
Answer: ABE
NEW QUESTION 15
Which modification needs to be made to the Service Management Facility before you publish a new package to the IPS repository?
- A. The pkg.depotd must be disabled.
- B. The pkg/readonly property for the application/pkg/server service must be set to false.
- C. The Pkg/writabie_root property for the application/Pkg/server service must be set to true.
- D. The pkg/image.root property for the application/pkg/server service must be set to the location of the repository.
Answer: D
Explanation:
pkg/image_root
(astring) The path to the image whose file information will be used as a cache for file data.
NEW QUESTION 16
You start to execute a program by using the following command:
~/bigscript &
You then determine that the process is not behaving as expected, and decide that you need to terminate the process.
Based on the information shown below, what is the process number you should terminate?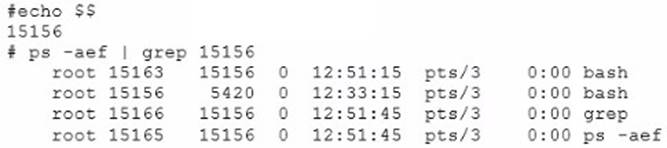
- A. 15163
- B. 15156
- C. 15166
- D. 15165
Answer: A
Explanation:
From the output exhibit we can deduce that the shell has id 15156. It has spawned three subprocesses:
grep: id 15166
ps –aef 15165
The remaining 15163 must be the subshell (see note below). This is the id of the process which should be terminated.
NEW QUESTION 17
You are logged in as root to a newly installed Solaris 11 system. You issue the command useradd -d, and then examine the /usr/sadm/defadduser file. This file includes the entry defshell=/bin/sh. Which shell will now be the default for the next account created?
- A. bash shell
- B. C shell
- C. korn shod
- D. bourne shell
Answer: A
Explanation:
Oracle Solaris 11 introduces user environment and command-line argument changes that include the following:
* Shell changes - The default shell, /bin/sh, is now linked to ksh93. The default user shell is the Bourne-again (bash) shell.
* The legacy Bourne shell is available as /usr/sunos/bin/sh.
* The legacy ksh88 is available as /usr/sunos/bin/ksh from the shell/ksh88 package.
* Korn shell compatibility information is available in /usr/share/doc/ksh/COMPATIBILITY.
NEW QUESTION 18
Which two statements are true when updating Solaris 11 from one Support Respository Update (SRU) to another SRU by using the pkg update command?
- A. By default, the pkg update command automatically creates a backup Boot Environment whenever the kernel is affected by the update.
- B. By default, the pkg update command automatically creates a new Boot Environment whenever the kernel is affected by the update.
- C. The pkg update command can only be used to update to a newer SRU.
- D. The pkg update command can be used to update to a newer or older SRU.
- E. By default, the pkg update command always updates Solaris 11 to the first SRU that was released after the Current SRU.
- F. The pkg update command can only be performed while running in the single-user milestone.
Answer: BC
NEW QUESTION 19
You created a new zpool. Now you need to migrate the existing ZFS file system from pool1/prod to pool2/prod.
You have these requirements:
1. Users must have access to the data during the migration, so you cannot shutdown the file system while the migration takes place.
2. Because you want to copy the data as quickly as possible, you need to increase the server resources devoted to the ZFS migration.
Which method would you use to modify the ZFS shadow migration daemon defaults to increase the concurrency and overall speed of migration?
- A. Svccfg - s filesystem/shadowd:defaultsetprop config_params/shadow_threads=integer: 16endsvcadm refresh filesystem/shadowd: default
- B. Specify the -b <blocksize> option with the zfs create command and increase the value of<blocksize>
- C. Use the -o -volblocksize=<blocksize>option with the zfs create command and increase the value of the default <blocksize>.
- D. Svccfg -s filesystem/zfs: defaultsetprop config_params/shadow_threads = integer: 16endsvcadm refresh filesystem/zfs:default
Answer: A
Explanation:
shadowd is a daemon that provides background worker threads to migrate data for a shadow migration. A shadow migration gradually moves data from a source file system into a new “shadow” file system. Users can access and change their data within the shadow file system while migration is occurring.
The shadowd service is managed by the service management facility, smf(5).
Administrative actions on this service, such as enabling, disabling, or requesting restart, can be performed using svcadm(1M). The service's status can be queried using the svcs(1) command.
The svccfg(1M) command can be used to manage the following parameter related to shadowd:
config_params/shadow_threads
Note: Oracle Solaris 11: In this release, you can migrate data from an old file system to a new file system while simultaneously allowing access and modification of the new file system during the migration process.
Setting the shadow property on a new ZFS file system triggers the migration of the older data. The shadow property can be set to migrate data from the local system or a remote system with either of the following values:
file:///path nfs://host:path
NEW QUESTION 20
The storage pool configuration on your server is:
You back up the /pool1/data file system, creating a snapshot and copying that snapshot to tape (/dev/rmt/0). You perform a full backup on Sunday night and Incremental backups on Monday through Saturday night at 11:00 pm. Each incremental backup will copy only the data that has been modified since the Sunday backup was started.
On Thursday, at 10:00 am, you had a disk failure. You replaced the disk drive (c4t0d0). You created pool (pool1) on that disk.
Which option would you select to restore the data in the /pool1/data file system?
- A. zfs create pool1/dataLoad the Monday tape and enter:zfs recv pool1/data </dev/rmt/0Load the Wednesday tape and enter:zfs recv –F pool1/data < /dev/rmt/0
- B. Load the Sunday tape and restore the Sunday snapshot:zfs recv pooll/data </dev/rmt/0zfs rollback pool1/data@monLoad the Wednesday tape and restore the Wednesday snapshot:zfs recv –i pooll/data < /dev/rmt/0zfs rollback pool1/data@wed
- C. zfs create pooll/dataLoad the Wednesday tape and enter:zfs recv -F pool1/data </dev/rmt/0
- D. Load the Sunday tape and enter:zfs recv pool1/data < /dev/rmt/0Load the Wednesday tape and enter:* commands missing*
Answer: D
Explanation:
First the full backup must be restored. This would be the Sunday backup.
Then the last incremental backup must be restored. This would be the Wednesday backup. Before restoring the Wednesday incremental file system snapshot, the most recent snapshot must first be rolled back.
By exclusion D) would be best answer even though it is incomplete.
NEW QUESTION 21
You are troubleshooting the failure of a computer to mount an NFS file system hosted by a server (hostname mars) in the local area network.
Select the three commands that will enable you to identify the problem.
- A. ping - s mars
- B. cat /etc/vfstab
- C. cat /etc/dfs/dfstab
- D. sharemgr show -v
- E. showmount -e mars
- F. rpcinfo -s mars | egrep ‘nfs|mountd’
Answer: BEF
Explanation:
B: The mount point Error. The following message appears during the boot process or in response toan explicit mount request and indicates a non-existent mount point.
Mount: mount-point /DS9 does not exist.
To solve the mount point error condition, check that the mount point exists on the client. Check the spelling of the mount point on the command line or in the /etc/vfstab file (B) on the client, or comment outthe entry and reboot the system.
Note: The /etc/vfstab file lists all the file systems to be automatically mounted at system boot time, with the exception of the /etc/mnttab and /var/run file systems.
E: showmount
This command displays all clients that have remotely mounted file systems that are shared from an NFS server, or only the file systems that are mounted by clients, or the shared file systems with the client access information. The command syntax is:
showmount [ -ade ] [ hostname ]
where -a prints a list of all the remote mounts (each entry includes the client name and the
directory), -d prints a list of the directories that are remotely mounted by clients, -e prints a list of the files shared (or exported), and hostname selects the NFS server to gather the information from. If hostname is not specified the local host is queried.
F: * mountd Daemon
This daemon handles file-system mount requests from remote systems and provides access control. The mountd daemon checks /etc/dfs/sharetab to determine which file systems are available for remote mounting and which systems are allowed to do the remote mounting.
* Commands for Troubleshooting NFS Problems
These commands can be useful when troubleshooting NFS problems. rpcinfo Command
This command generates information about the RPC service that is running on a system.
NEW QUESTION 22
Review the storage pool information:
Which statement describes the status of this storage pool?
- A. It is a RAIDZ storage pool and can withstand a single disk failure; data will be striped at: disk components.
- B. It is a double-parity RAIDZ storage pool and can withstand two disk failures; data will be striped across four disk components.
- C. It is an improperly configured RAIDZ storage pool; data will be striped across four disk components, but only three drives are protected with redundancy.
- D. It is an improperly configured RAIDZ storage pool; data will be striped across three disk components, but only three drives are protected with redundancy.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Device c3t6d0 is not included in the RAIDZ storage pool. The other three devices are included in the raidz pool. The data on these devices are protected.
Note: In addition to a mirrored storage pool configuration, ZFS provides a RAID-Z configuration with either single, double, or triple parity fault tolerance. Single-parity RAID-Z (raidz or raidz1) is similar to RAID-5. Double-parity RAID-Z (raidz2) is similar to RAID-6.
NEW QUESTION 23
You have installed an update to the gzip package and need to "undo" .ho update and return the package to its "as-delivered" condition. Which command would you use?
- A. pkg undo
- B. pkg revert
- C. pkg fix
- D. pkg uninstall
Answer: B
Explanation:
Use the pkg revert command to restore files to their as-delivered condition.
NEW QUESTION 24
You have been asked to do an orderly shutdown on a process with a PID of 1234, with the kill command.
Which command is best?
- A. kill -2 1234
- B. kill -15 1234
- C. kill -9 1234
- D. kill -1 1234
Answer: B
Explanation:
On POSIX-compliant platforms, SIGTERM is the signal sent to a process to request its termination. The symbolic constant for SIGTERM is defined in the header file signal.h. Symbolic signal names are used because signal numbers can vary across platforms, however on the vast majority of systems, SIGTERM is signal #15.
SIGTERM is the default signal sent to a process by the kill or killall commands. It causes the termination of a process, but unlike the SIGKILL signal, it can be caught and interpreted (or ignored) by the process. Therefore, SIGTERM is akin to asking a process to terminate nicely, allowing cleanup and closure of files. For this reason, on many Unix systems during shutdown, init issues SIGTERM to all processes that are not essential to powering off, waits a few seconds, and then issues SIGKILL to forcibly terminate any such processes that remain.
NEW QUESTION 25
dbzone is currently running on your server.
Which two methods would you use to safely and cleanly shut down dbzone and all of its applications?
- A. zlogin –z dbzone halt
- B. zoneadm –z dbzone shutdown –i0
- C. zoneadm –z dbzone shutdown
- D. zoneadm –z dbzone halt
- E. zlogin dbzone shutdown –i0
Answer: DE
Explanation:
D: zoneadm halt command halts the specified zones. halt bypasses running the shutdown
scripts inside the zone. It also removes run time resources of the zone.
E: Use: zlogin zone shutdown
to cleanly shutdown the zone by running the shutdown scripts.
Use this procedure to cleanly shut down a zone.
1. Become superuser, or assume the Primary Administrator role.
2. Log in to the zone to be shut down, for example, my-zone, and specify shutdown as the name of the utility and init 0 as the state global# zlogin my-zone shutdown -y -g0 -i 0
NEW QUESTION 26
Review the ZFS dataset output that is displayed on your system:
Which four correctly describe the output?
- A. /data/file4 has been added.
- B. The link /data/file3 has been added.
- C. /data/file3 has been renamed to /data/file13.
- D. /data/file4 has been modified and is now larger.
- E. /data/file1 has been deleted.
- F. /data/file1 has been modified and is now smaller.
- G. /data/file5 has been modified.
- H. /data/file3 (a link) has been removed.
Answer: ACEG
Explanation:
A: + Indicates the file/directory was added in the later dataset
C: R Indicates the file/directory was renamed in the later dataset E: - Indicates the file/directory was removed in the later dataset
G: M Indicates the file/directory was modified in the later dataset
Note: Identifying ZFS Snapshot Differences (zfs diff)
You can determine ZFS snapshot differences by using the zfs diff command.
The following table summarizes the file or directory changes that are identified by the zfs diff command.
File or Directory Change Identifier
* File or directory is modified or file or directory link changed M
* File or directory is present in the older snapshot but not in the newer snapshot
—
* File or directory is present in the newer snapshot but not in the older snapshot
+
* File or directory is renamed R
NEW QUESTION 27
Which two are true about accounts, groups, and roles in the Solaris user database?
- A. All Solaris user accounts must have a unique UID number.
- B. A Solaris account name may be any alphanumeric string, and can have a maximum length of 8 characters.
- C. Account UID numbers 0-09 are system-reserved.
- D. The GID for an account determines the default group ownership of new files created by that account.
- E. The groups that an account is a member of are determined by the entries in the/etc/group file.
Answer: AB
Explanation:
A: Solaris uses a UID (User ID) to identify each user account. The UID is a unique number assigned to each user. It is usually assigned by the operating system when the account is created.
B: In Solaris the account name can include any alphanumeric string (and . _ -). The maximum length is 8 characters.
NEW QUESTION 28
Which option displays the result of running the zfs list command?
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer: B
Explanation:
The zfs list command provides an extensible mechanism for viewing and querying dataset information.
You can list basic dataset information by using the zfs list command with no options. This command displays the names of all datasets on the system and the values of their used, available, referenced, and mountpoint properties. For more information about these properties, see Introducing ZFS Properties.
For example:
# zfs list
NAME USED AVAIL REFER MOUNTPOINT
pool 476K 16.5G 21K /pool
pool/clone 18K 16.5G 18K /pool/clone pool/home 296K 16.5G 19K /pool/home
pool/home/marks 277K 16.5G 277K /pool/home/marks pool/home/marks@snap 0 - 277K -
pool/test 18K 16.5G 18K /test
NEW QUESTION 29
......
Thanks for reading the newest 1Z0-821 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM Dumps-hub.com 1Z0-821 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.dumps-hub.com/1Z0-821-dumps.html (243 Q&As Dumps)
- What 100% Correct 1Z0-447 dumps Is?
- High Quality 1z0-082 Bundle 2021
- Top Tips Of Avant-garde 1z0-1049 Exam Price
- Precise 1Z0-809 Exam Dumps 2021
- Approved 1z0-900 Guidance 2021
- 100% Correct 1Z0-063 Dumps Questions 2021
- how many questions of 1z0-052 exam?
- The Rebirth Guide To 1Z0-821 Test Questions
- Most Recent 1z0-931 Keys 2021
- Oracle 1Z0-053 Braindumps 2021


