70-640 Exam Questions - Online Test
70-640 Premium VCE File

150 Lectures, 20 Hours
are updated and are verified by experts. Once you have completely prepared with our you will be ready for the real 70-640 exam without a problem. We have . PASSED First attempt! Here What I Did.
Free demo questions for Microsoft 70-640 Exam Dumps Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains several domain controllers.
You need to modify the Password Replication Policy on a read-only domain controller (RODC).
Which tool should you use?
- A. Group Policy Management
- B. Active Directory Domains and Trusts
- C. Active Directory Users and Computers
- D. Computer Management
- E. Security Configuration Wizard
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/rodc-guidance-for-administering-the-password-
replication-policy.aspx
Administering the Password Replication Policy
This topic describes the steps for viewing, configuring, and monitoring the Password Replication Policy (PRP) and password caching for read-only domain controllers (RODCs). To configure the PRP using Active Directory Users and Computers
1. Open Active Directory Users and Computers as a member of the Domain Admins group.
2. Ensure that you are connected to a writeable domain controller running Windows Server 2008 in the correct domain.
3. Click Domain Controllers, and in the details pane, right-click the RODC computer account, and then click Properties.
4. Click the Password Replication Policy tab.
5. The Password Replication Policy tab lists the accounts that, by default, are defined in the Allowed list and the Deny list on the RODC. To add other groups that should be included in either the Allowed list or the Deny list, click Add.
To add other accounts that will have credentials cached on the RODC, click Allow passwords for the account to replicate to this RODC.
To add other accounts that are not allowed to have credentials cached on the RODC, click Deny passwords for the account from replicating to this RODC.
NEW QUESTION 2
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The functional level of the forest is Windows Server 2008 R2.
You have four Active Directory sites. Each site has multiple Active Directory subnets.
You need to identify all of the authentication requests that originate from client computers that are not associated to an Active Directory subnet.
What should you use?
- A. The %Systemroot%System32Network_llu.log log file
- B. The %Systemroot%DebugNetsetup.log log file
- C. The Authentication User Interface operational log
- D. The %Systemroot%DebugNetlogon.log log file
Answer: B
Explanation:
Identifying Whether You Have a Problem Authenticating You can identify whether you have a problem authenticating (or joining) a computer to a domain by verifying that the local workstation is working. Do this by running the Netdiag tool. Read the output from the top, and look for the words "ERROR" or "FATAL." (Many failures are not relevant to the domain itself; but you should follow up on them because they involve network connectivity issues.) If you don't find these words in the output, continue as follows: Run netdiag /v (verbose mode). Do you receive any specific error messages or FATAL errors? If the answer to the preceding question is "No," run netdiag /debug. Do you receive any specific error messages or FATAL errors? If Netdiag displays an error or failure with the domain itself, check the % SystemRoot %debugnetsetup.log file for join errors.
NEW QUESTION 3
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain is configured as shown in the following table.
Users in Branch2 sometimes authenticate to a domain controller in Branch1.
You need to ensure that users inBranch2 only authenticate to the domain controllers in
Main.
What should you do?
- A. On DC3, set the AutoSiteCoverage value to 0.
- B. On DC3, set the AutoSiteCoverage value to 1.
- C. On DC1 and DC2, set the AutoSiteCoverage value to 0.
- D. On DC1 and DC2, set the AutoSiteCoverage value to 1.
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 4
HOTSPOT
Your network contains an Active Directory forest. The DNS infrastructure fails.
You rebuild the DNS infrastructure.
You need to force the registration of the Active Directory Service Locator (SRV) records in DNS.
Which service should you restart on the domain controllers? To answer, select the appropriate service in the answer area. 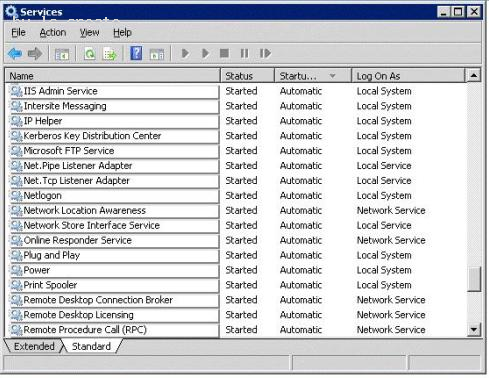
Answer:
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 5
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains five domain controllers. A domain controller named DC1 has the DHCP role and the file server role installed.
You need to move the Active Directory database on DC1 to an alternate location.The solution must minimize impact on the network during the database move.
What should you do first?
- A. Restart DC1 in Safe Mod
- B. Restart DC1 in Directory Services Restore Mod
- C. Start DC1 from Windows P
- D. Stop the Active Directory Domain Services service on DC1.
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc794895%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Relocating the Active Directory Database Files Applies To: Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2 Relocating Active Directory database files usually involves moving files to a temporary location while hardware updates are being performed and then moving the files to a permanent location. On domain controllers that are running versions of Windows 2000 Server and Windows Server 2003, moving database files requires restarting the domain controller in Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM). Windows Server 2008 introduces restartable Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), which you can use to perform database management tasks without restarting the domain controller in DSRM. Before you move database files, you must stop AD DS as a service.
NEW QUESTION 6
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains two domain controllers named DC1 and DC2. DC1 hosts a standard primary DNS zone for the domain. Dynamic updates are enabled on the zone. DC2 hosts a standard secondary DNS zone for the domain.
You need to configure DNS to allow only secure dynamic updates.
What should you do first?
- A. On DC1 and DC2, configure a trust ancho
- B. On DC1 and DC2, configure a connection security rul
- C. On DC1, configure the zone transfer setting
- D. On DC1, configure the zone to be stored in Active Director
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/shorttutorials/configuring-dns-server-for-secure-only-dynamic-updates/ Configuring DNS Server for Secure Only Dynamic Updates About Dynamic Updates During the installation of Active Directory Domain Services on Windows Server 2008 R2, the installation process automatically installs the DNS server on the computer, in case it does not already exist in the network. After the successful installation of Active Directory Domain Services, the DNS server is by default configured to automatically update the records of only the domain client computers as soon as it receives the registration request from them. This automatic update of DNS records in the DNS database is technically known as ‘Dynamic Updates’. Types of DNS Updates Dynamic updates that DNS server in Windows Server 2008 R2 supports include: Nonsecure and Secure – When this type of dynamic update is selected, any computer can send registration request to the DNS server. The DNS server in return automatically adds the record of the requesting computer in the DNS database, even if the computer does not belong to the same DNS domain. Although this configuration remarkably reduces administrative overhead, this setting is not recommended for the organizations that have highly sensitive information available in the computers. Secure only – When this type of dynamic update is selected, only the computers that are members of the DNS domain can register themselves with the DNS server. The DNS server automatically rejects the requests from the computers that do not belong to the domain. This protects the DNS server from getting automatically populated with records of unwanted, suspicious and/or fake computers. None – When this option is selected, the DNS server does not accept any registration request from any computers whatsoever. In such cases, DNS administrators must manually add the IP addresses and the Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) of the client computers to the DNS database. In most production environments, systems administrators configure Secure Only dynamic updates for DNS. This remarkably reduces the security risks by allowing only the authentic domain client computers to register themselves with the DNS server automatically, and decreases the administrative overhead at the same time. However in some scenarios, administrators choose to have non-Active Directory integrated zone to stay compliant with the policies of the organization. This configuration is not at all recommended because it does not allow administrators to configure DNS server for Secure only updates, and it does not allow the DNS database to get replicated automatically to the other DNS servers along with the Active Directory replication process. When DNS zone is not Active Directory integrated, DNS database replication process must be performed manually by the administrators. Configure Secure Only Dynamic Updates in Windows Server 2008 R2 DNS Server To configure Secure Only dynamic DNS updates in Windows Server 2008 R2, administrators must follow the steps given as below:
1. Log on to Windows Server 2008 R2 DNS server computer with the domain admin or enterprise admin account on which ‘Secure only’ dynamic updates are to be configured.
2. On the desktop screen, click Start.
3. From the Start menu, go to Administrator Tools > DNS.
4. On DNS Manager snap-in, from the console tree in the left, double-click to expand the DNS server name.
5. From the expanded list, double-click Forward Lookup Zones.
6. From the displayed zones list, right-click the DNS zone on which secure only dynamic updates are to be configured.
7. From the displayed context menu, click Properties. 
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
8. On the zone’s properties box, make sure that the General tab is selected.
9. On the selected tab, choose Secure only option from the Dynamic updates drop-down
list.
Note: Secure only option is available only if the DNS zone is Active Directory integrated. 
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Secure Only Dynamic Update
10. Click OK to apply the modified changes.
11. Close DNS Manager snap-in when done.
NEW QUESTION 7
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains two file servers. The file servers are configured as shown in the following table.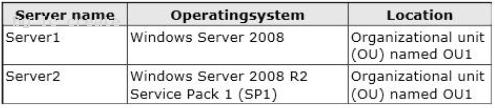
You create a Group Policy object (GPO) named GPO1 and you link GPO1 to OU1.
You configure the advanced audit policy as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.) 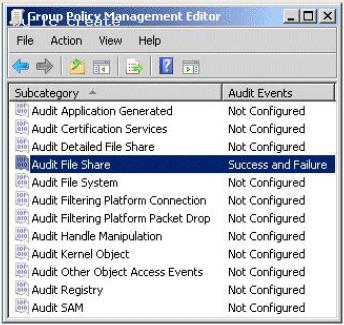
You discover that the settings are not applied to Server1. The settings are applied to
Server2.
You need to ensure that access to the file shares on Server1 is audited.
What should you do?
- A. On Server1, run secedit.exe and specify the /configure paramete
- B. On Server1, run auditpol.exe and specify the /set paramete
- C. From GPO1, configure the Security Option
- D. From Active Directory Users and Computers, modify the permissions of the computer account for Server1.
- E. From Active Directory Users and Computers, add Server1 to the Event Log Readers grou
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 8
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains four domain controllers.
You modify the Active Directory schema.
You need to verify that all the domain controllers received the schema modification.
Which command should you run?
- A. netdom.exe query fsmo
- B. repadmin.exe /showrepl *
- C. dcdiag.exe /e /test:Topology
- D. dcdiag.exe /a
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 9
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a file server named Server1. Server1 has a shared folder named Profiles.
You plan to create a new user template named User_Template.
You need to ensure that when you copy User_Temptate, the new user account has a unique profile folder created in the Profiles share.
Which value should you specify for the profile path?
- A. %Userprofile%Server1profiles
- B. \Server1profiles%username%
- C. \Server1%userprofile%
- D. \Server1profilesusername
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 10
Your company network has an Active Directory forest that has one parent domain and one child domain. The child domain has two domain controllers that run Windows Server 2008. All user accounts from the child domain are migrated to the parent domain. The child domain is scheduled to be decommissioned.
You need to remove the child domain from the Active Directory forest.
What are two possible ways to achieve this goal? (Each correct answer presents a complete solution. Choose two.)
- A. Run the Computer Management console to stop the Domain Controller service on both domain controllers in the child domai
- B. Delete the computer accounts for each domain controller in the child domai
- C. Remove the trust relationship between the parent domain and the child domai
- D. Use Server Manager on both domain controllers in the child domain to uninstall the Active Directory domain services rol
- E. Run the Dcpromo tool that has individual answer files on each domain controller in the child domai
Answer: CD
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc755937%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Decommissioning a Domain Controller To complete this task, perform the following procedures:
1. View the current operations master role holders
2. Transfer the schema master
3. Transfer the domain naming master
4. Transfer the domain-level operations master roles
5. Determine whether a domain controller is a global catalog server
6. Verify DNS registration and functionality
7. Verify communication with other domain controllers
8. Verify the availability of the operations masters
9. If the domain controller hosts encrypted documents, perform the following procedure before you remove Active Directory to ensure that the encrypted files can be recovered after Active Directory is removed: Export a certificate with the private key 10.Uninstall Active Directory 11.If the domain controller hosts encrypted documents and you backed up the certificate and private key before you remove Active Directory, perform the following procedure to re-import the certificate to the server: Import a certificate
12. Determine whether a Server object has child objects
13. Delete a Server object from a site
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc737258%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Uninstall Active Directory To uninstall Active Directory
1. Click Start, click Run, type dcpromo and then click OK.
NEW QUESTION 11
Your company has an Active Directory domain named ad.contoso.com. The domain has two domain controllers named DC1 and DC2. Both domain controllers have the DNS server role installed.
You install a new DNS server named DNS1.contoso.com on the perimeter network. You configure DC1 to forward all unresolved name requests to DNS1.contoso.com.
You discover that the DNS forwarding option is unavailable on DC2.
You need to configure DNS forwarding on the DC2 server to point to the DNS1.contoso.com server.
Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
Choose two.)
- A. Clear the DNS cache on DC2.
- B. Configure conditional forwarding on DC2.
- C. Configure the Listen On address on DC2.
- D. Delete the Root zone on DC2.
Answer: BD
Explanation:
Answer: Delete the Root zone on DC2. Configure conditional forwarding on DC2.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754941.aspx Configure a DNS Server to Use Forwarders A forwarder is a Domain Name System (DNS) server on a network that is used to forward DNS queries for external DNS names to DNS servers outside that network. You can also configure your server to forward queries according to specific domain names using conditional forwarders. http://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/winserverNIS/thread/0ca38ece-d76e-42f0-85d5-a342f9e169f5/ Deleting .root dns zone in 2008 DNS
Q: We have 2 domain controllers and .root zone is created in the DNS. Due to which the external name resolution is not possible. I had tried to add conditional forwarders but i get an error saying that conditional forwarders cannot be created on root DNS servers. A 1: If you have a "root" zone created in your DNS, and you no longer want that configuration, you can just simply delete that zone. There is no reason to have a root "." zone hosted unless you want to make sure that the DNS server is authoritative for all queries and not allow the DNS server to go elsewhere for name resolution.
If you delete this zone, the DNS server will be able to use its root hints, or fowarders to resolve queries for zones its not authoritative for. A 2: That was from the old 2000 days where DCPROMO would create it if it detected no internet access while promoting the first DC. Jut remove it, and the Forwarders option reappear.
Further information: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/298148
How To Remove the Root Zone (Dot Zone)
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731879%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Reviewing DNS Concepts Delegation For a DNS server to answer queries about any name, it must have a direct or indirect path to every zone in the namespace. These paths are created by means of delegation. A delegation is a record in a parent zone that lists a name server that is authoritative for the zone in the next level of the hierarchy. Delegations make it possible for servers in one zone to refer clients to servers in other zones. The following illustration shows one example of delegation. 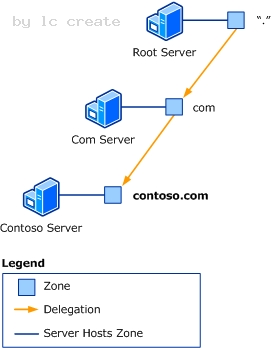
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
The DNS root server hosts the root zone represented as a dot ( . ). The root zone contains a delegation to a zone in the next level of the hierarchy, the com zone. The delegation in the root zone tells the DNS root server that, to find the com zone, it must contact the Com server. Likewise, the delegation in the com zone tells the Com server that, to find the contoso.com zone, it must contact the Contoso server. Note: A delegation uses two types of records. The name server (NS) resource record provides the name of an authoritative server. Host (A) and host (AAAA) resource records provide IP version 4 (IPv4) and IP version 6 (IPv6) addresses of an authoritative server. This system of zones and delegations creates a hierarchical tree that represents the DNS namespace. Each zone represents a layer in the hierarchy, and each delegation represents a branch of the tree. By using the hierarchy of zones and delegations, a DNS root server can find any name in the DNS namespace. The root zone includes delegations that lead directly or indirectly to all other zones in the hierarchy. Any server that can query the DNS root server can use the information in the delegations to find any name in the namespace.
NEW QUESTION 12
A corporate network includes an Active Directory-integrated zone. All DNS servers that host the zone are domain controllers.
You add multiple DNS records to the zone.
You need to ensure that the new records are available on all DNS servers as soon as possible.
Which tool should you use?
- A. Ldp
- B. Repadmin
- C. Ntdsutil
- D. Nslookup
- E. Active Directory Sites And Services console
- F. Active Directory Domains And Trusts console
- G. Dnslint
- H. Dnscmd
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc811569.aspx
Forcing Replication
Sometimes it becomes necessary to forcefully replicate objects and entire partitions
between domain controllers that may or may not have replication agreements.
Force a replication event with all partners
The repadmin /syncall command synchronizes a specified domain controller with all
replication partners.
Syntax
repadmin /syncall <DC> [<NamingContext>] [<Flags>]
Parameters
<DC>
Specifies the host name of the domain controller to synchronize with all replication
partners.
<NamingContext>
Specifies the distinguished name of the directory partition.
<Flags>
Performs specific actions during the replication.
NEW QUESTION 13
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. You have a management computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 7.
You need to forward the logon events of all the domain controllers in contoso.com to Computer1.
All new domain controllers must be dynamically added to the subscription.
What should you do?
- A. From Computer1, configure source-initiated event subscription
- B. From a Group Policy object (GPO) linked to the Domain Controllers organizational unit (OU), configure the Event Forwarding nod
- C. From Computer1, configure collector-initiated event subscription
- D. From a Group Policy object (GPO) linked to the Domain Controllers organizational unit (OU), configure the Event Forwarding nod
- E. From Computer1, configure source-initiated event subscription
- F. Install a server authentication certificate on Computer1. Implement autoenrollment for the Domain Controllers organizational unit (OU).
- G. From Computer1, configure collector-initiated event subscription
- H. Install a server authentication certificate on Computer1. Implement autoenrollment for the Domain Controllers organizational unit (OU).
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/bb870973(v=vs.85).aspx
Setting up a Source Initiated Subscription
Source-initiated subscriptions allow you to define a subscription on an event collector computer without defining the event source computers, and then multiple remote event source computers can be set up (using a group policy setting) to forward events to the event collector computer. This differs from a collector initiated subscription because in the collector initiated subscription model, the event collector must define all the event sources in the event subscription.
NEW QUESTION 14
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com.
The domain contains an enterprise certification authority (CA).
You plan to deploy certificates to all of the domain users. The certificates will be based on a custom Smartcard Logon template.
You need to recommend a solution to ensure that the users can log on to the domain by using smart cards.
What should you include in the recommendation?
- A. From Certificate Templates, set the minimum certificate key size to 512.
- B. From Active Directory Users and Computers, select Use Kerberos DES encryption types for this accoun
- C. From Certificate Templates, include the user principal name (UPN) in the subject alternate name (SAN) of the templat
- D. From Active Directory Users and Computers, configure Published Certificates for user account
Answer: C
Explanation: Request a smart card certificate from the third-party CA.
Enroll for a certificate from the third-party CA that meets the stated requirements. The
method for enrollment varies by the CA vendor.
The smart card certificate has specific format requirements:
* Subject Alternative Name = Other Name: Principal Name= (UPN). For example:
UPN = user1@name.com
The UPN OtherName OID is : "1.3.6.1.4.1.311.20.2.3"
The UPN OtherName value: Must be ASN1-encoded UTF8 string
* Subject = Distinguished name of user.
* The CRL Distribution Point (CDP) location (where CRL is the Certification Revocation List) must be populated, online, and available.
* Key Usage.= Digital Signature
* Basic Constraints.[Subject Type=End Entity, Path Length Constraint=None] (Optional)
* Enhanced Key Usage
NEW QUESTION 15
You have a domain controller named DC1 that runs Windows Server 2008 R2. DC1 is
configured as a DNS Server for contoso.com.
You install the DNS Server role on a member server named Server1 and then you create a
standard secondary zone for contoso.com.
You configure DC1 as the master server for the zone.
You need to ensure that Server1 receives zone updates from DC1.
What should you do?
- A. On DC1, modify the permissions of contoso.com zon
- B. On Server1, add a conditional forwarde
- C. On DC1, modify the zone transfer settings for the contoso.com zon
- D. Add the Server1 computer account to the DNSUpdateProxy grou
Answer: C
Explanation: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc771652.aspx
Modify Zone Transfer Settings You can use the following procedure to control whether a zone will be transferred to other servers and which servers can receive the zone transfer.
To modify zone transfer settings using the Windows interface
1. Open DNS Manager.
2. Right-click a DNS zone, and then click Properties.
3. On the Zone Transfers tab, do one of the following:
To disable zone transfers, clear the Allow zone transfers check box.
To allow zone transfers, select the Allow zone transfers check box.
4. If you allowed zone transfers, do one of the following:
To allow zone transfers to any server, click To any server.
To allow zone transfers only to the DNS servers that are listed on the Name Servers tab,
click Only to servers listed on the Name Servers tab.
To allow zone transfers only to specific DNS servers, click Only to the following servers,
and then add the IP address of one or more DNS servers.
NEW QUESTION 16
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com.
You plan to deploy a child domain named sales.contoso.com.
The domain controllers in sales.contoso.com will be DNS servers for sales.contoso.com.
You need to ensure that users in contoso.com can connect to servers in sales.contoso.com by using fully qualified domain names (FQDNs).
What should you do?
- A. Create a DNS forwarde
- B. Create a DNS delegatio
- C. Configure root hint server
- D. Configure an alternate DNS server on all client computer
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc784494%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Delegating zones DNS provides the option of dividing up the namespace into one or more zones, which can then be stored, distributed, and replicated to other DNS servers. When deciding whether to divide your DNS namespace to make additional zones, consider the following reasons to use additional zones: A need to delegate management of part of your DNS namespace to another location or department within your organization. A need to divide one large zone into smaller zones for distributing traffic loads among multiple servers, improve DNS name resolution performance, or create a more fault-tolerant DNS environment. A need to extend the namespace by adding numerous subdomains at once, such as to accommodate the opening of a new branch or site. If, for any of these reasons, you could benefit from delegating zones, it might make sense to restructure your namespace by adding additional zones. When choosing how to structure zones, you should use a plan that reflects the structure of your organization. When delegating zones within your namespace, be aware that for each new zone you create, you will need delegation records in other zones that point to the authoritative DNS servers for the new zone. This is necessary both to transfer authority and to provide correct referral to other DNS servers and clients of the new servers being made authoritative for the new zone. When a standard primary zone is first created, it is stored as a text file containing all resource record information on a single DNS server. This server acts as the primary master for the zone. Zone information can be replicated to other DNS servers to improve fault tolerance and server performance. When structuring your zones, there are several good reasons to use additional DNS servers for zone replication:
1. Added DNS servers provide zone redundancy, enabling DNS names in the zone to be resolved for clients if a primary server for the zone stops responding.
2. Added DNS servers can be placed so as to reduce DNS network traffic. For example, adding a DNS server to the opposing side of a low-speed WAN link can be useful in managing and reducing network traffic.
3. Additional secondary servers can be used to reduce loads on a primary server for a zone. Example: Delegating a subdomain to a new zone As shown in the following figure, when a new zone for a subdomain (example.microsoft.com) is created, delegation from the parent zone (microsoft.com) is needed.
In this example, an authoritative DNS server computer for the newly delegated example.microsoft.com subdomain is named based on a derivative subdomain included in the new zone (ns1.us.example.microsoft.com). To make this server known to others outside of the new delegated zone, two RRs are needed in the microsoft.com zone to complete delegation to the new zone. These RRs include: An NS RR to effect the delegation. This RR is used to advertise that the server named ns1.us.example.microsoft.com is an authoritative server for the delegated subdomain. An A RR (also known as a glue record) is needed to resolve the name of the server specified in the NS RR to its IP address. The process of resolving the host name in this RR to the delegated DNS server in the NS RR is sometimes referred to as glue chasing. Note When zone delegations are correctly configured, normal zone referral behavior can sometimes be circumvented if you are using forwarders in your DNS server configuration.
NEW QUESTION 17
Your company has an Active Directory forest.
You plan to install an Enterprise certification authority (CA) on a dedicated stand-alone server.
When you attempt to add the Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) role, you find that the Enterprise CA option is not available.
You need to install the AD CS role as an Enterprise CA.
What should you do first?
- A. Add the DNS Server rol
- B. Add the Active Directory Lightweight Directory Service (AD LDS) rol
- C. Add the Web server (IIS) role and the AD CS rol
- D. Join the server to the domai
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc772393%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Active Directory Certificate Services Step-by-Step Guide
http://kazmierczak.eu/itblog/2012/09/23/enterprise-ca-option-is-greyed-out-unavailable/
Enterprise CA option is greyed out / unavailable Many times, administrators ask me what to do when installing Active Directory Certificate Services they cannot choose to install Enterprise Certification Authority, because it’s unavailable as in following picture: 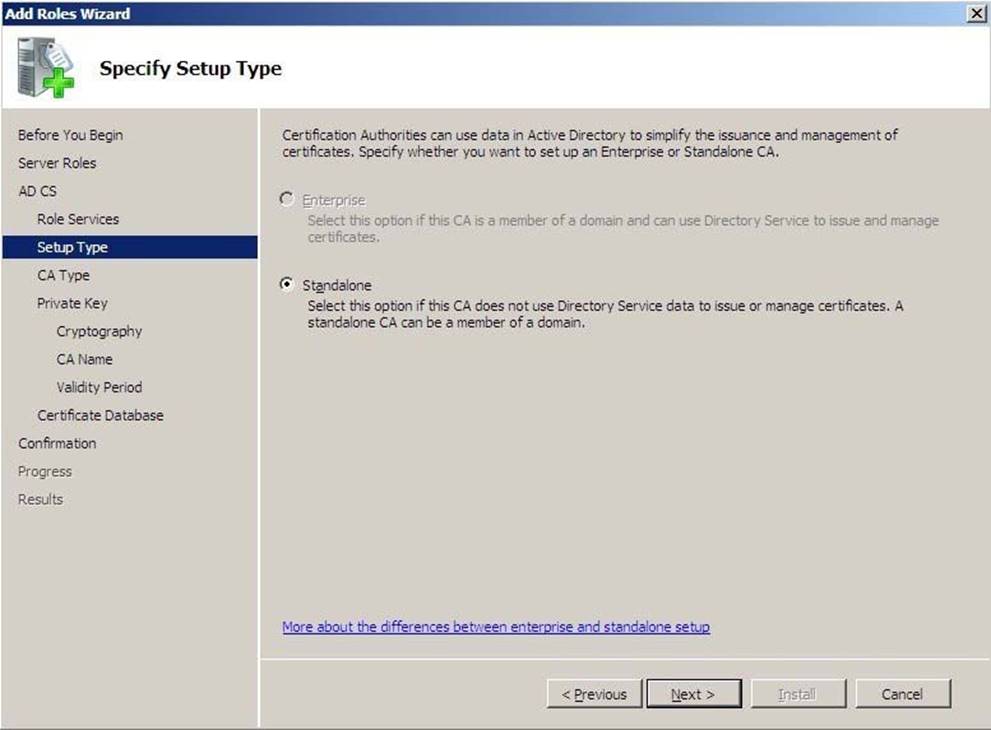
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Well, you need to fulfill basic requirements: Server machine has to be a member server (domain joined). You can run an Enterprise CA on the Standard, Enterprise, or Data Center Windows Edition. The difference is the number of ADCS features and components that can be enabled. To get full functionality, you need to run on Enterprise or Data Center Windows Server 2008 /R2/ Editions. It includes functionality like Role separation, Certificate manager restrictions, Delegated enrollment agent restrictions, Certificate enrollment across forests, Online Responder, Network Device Enrollment. In order to install an Enterprise CA, you must be a member of either Enterprise Admins or Domain Admins in the forest root domain (either directly or through a group nesting). If issue still persists, there is probably a problem with getting correct credentials of your account. There are many thing that can cause it (network blockage, domain settings, server configuration, and other issues). In all cases I got, this troubleshooting helped perfectly: First of all, carefully check all above requirements. Secondly, install all available patches and Service Packs with Windows Update before trying to install Enterprise CA. Check network settings on the CA Server. If there is no DNS setting, Certificate Authority Server cannot resolve and find domain. Sufficient privileges for writing the Enterprise CA configuration information in AD configuration partition are required. Determine if you are a member of the Enterprise Admins or Domain Admins in the forest root domain. Think about the account you are currently trying to install ADCS with. In fact, you may be sure, that your account is in Enterprise Admins group, but check this how CA Server “sees” your account membership by typing whoami /groups. You also need to be a member of local Administrators group. If you are not, you wouldn’t be able to run Server Manager, but still needs to be checked. View C:windowscertocm.log file. There you can find helpful details on problems with group membership. For example status of ENUM_ENTERPRISE_UNAVAIL_REASON_NO_INSTALL_RIGHTS indicates that needed memberships are not correct. Don’t forget to check event viewer on CA Server side and look for red lines. Verify that network devices or software&hardware firewalls are not blocking access from/to server and Domain Controllers. If so, Certificate Authority Server may not be communicating correctly with the domain. To check that, simply run nltest /sc_verify:DomainName Check also whether Server CA is connected to a writable Domain Controller. Enterprise Admins groups is the most powerful group and has ADCS required full control permissions, but who knows – maybe someone changed default permissions? Run adsiedit.msc on Domain Controller, connect to default context and first of all check if CN=Public Key Service,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=Your,DC=Domain,DC=Com container does exist. If so, check permissions for all subcontainers under Public Key Service if Enterprise Admins group has full control permissions. The main subcontainers to verify are Certificate Templates, OID, KRA containers. If no above tips help, disjoin the server from domain and join again. Ultimately reinstall operation system on CA Server.
NEW QUESTION 18
HOTSPOT
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains two sites named Seattle and Montreal. The Seattle site contains two domain controllers. The domain controllers are configured as shown in the following table. 
You need to enable universal group membership caching in the Seattle site.
Which object's properties should you modify?
To answer, select the appropriate object in the answer area. 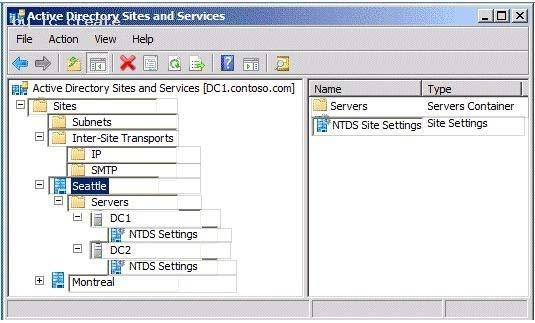
Answer:
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 19
Your company has an Active Directory domain. All consultants belong to a global group named TempWorkers.
The TempWorkers group is not nested in any other groups.
You move the computer objects of three file servers to a new organizational unit named SecureServers. These file servers contain only confidential data in shared folders.
You need to prevent members of the TempWorkers group from accessing the confidential data on the file servers.
You must achieve this goal without affecting access to other domain resources.
What should you do?
- A. Create a new GPO and link it to the SecureServers organizational uni
- B. Assign the Deny access to this computer from the network user right to the TempWorkers global grou
- C. Create a new GPO and link it to the domai
- D. Assign the Deny access to this computer from the network user right to the TempWorkers global grou
- E. Create a new GPO and link it to the domai
- F. Assign the Deny log on locally user right to the TempWorkers global grou
- G. Create a new GPO and link it to the SecureServers organizational uni
- H. Assign the Deny log on locally user right to the TempWorkers global grou
Answer: A
Explanation:
Personal comment:
Basically, you need to create a GPO for the Secure Servers and deny the TempWorkers
access to the shared folders (implies access from the network).
"Deny log on locally" makes no sense in this instance, because we are reffering to shared
folder and supposedly physical access to servers should be highly restricted.
And best practices recommend that you link GPOs at the domain level only for domain
wide purposes.
Thanks for reading the newest 70-640 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM 2passeasy 70-640 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/70-640/ (631 Q&As Dumps)
- What Exact 70-499 dumps Is?
- Approved Windows Server 70-532 braindumps
- Replace 70-412 Exam Study Guides With New Update Exam Questions
- All About Accurate PL-200 Free Question
- Replace Microsoft 70-413 exam question
- Printable AZ-100 Exam Questions and Answers 2021
- how many questions of 70-464 examcollection?
- how many questions of 70-483 exam question?
- Best Quality AZ-202 Exam Questions 2021
- The Secret of Microsoft 70-488 vce


