1Z0-051 Exam Questions - Online Test
1Z0-051 Premium VCE File

150 Lectures, 20 Hours
Cause all that matters here is passing exam with 1z0 051 latest dumps free download pdf. Cause all that you need is a high score of 1z0 051 practice test. The only one thing you need to do is downloading oracle 1z0 051 free now. We will not let you down with our money-back guarantee.
Oracle 1Z0-051 Free Dumps Questions Online, Read and Test Now.
NEW QUESTION 1
A data manipulation language statement _____.
- A. completes a transaction on a table
- B. modifies the structure and data in a table
- C. modifies the data but not the structure of a table
- D. modifies the structure but not the data of a table
Answer: C
Explanation:
modifies the data but not the structure of a table
Incorrect Answer:
ADML does not complete a transaction
BDDL modifies the structure and data in the table
DDML does not modified table structure.
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 8-3
NEW QUESTION 2
Which describes the default behavior when you create a table?
- A. The table is accessible to all user
- B. Tables are created in the public schem
- C. Tables are created in your schem
- D. Tables are created in the DBA schem
- E. You must specify the schema when the table is create
Answer: C
Explanation:
sorted by highest to lowest is DESCENDING order
Incorrect Answer: Agrant the table privilege to PUBLIC Blogin as sysoper Dlogin as DBA or sysdba Eno such option is allow.
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 9-9
NEW QUESTION 3
Examine the statement:
GRANT select, insert, update
ON student_grades
TO manager
WITH GRANT OPTION;
Which two are true? (Choose two.)
- A. MANAGER must be a rol
- B. It allows the MANAGER to pass the specified privileges on to other user
- C. It allows the MANAGER to create tables that refer to the STUDENT_GRADES tabl
- D. It allows the MANAGER to apply all DML statements on the STUDENT_GRADES tabl
- E. It allows the MANAGER the ability to select from, insert into, and update the STUDENT_GRADES tabl
- F. It allows the MANAGER the ability to select from, delete from, and update the STUDENT_GRADES tabl
Answer: BE
Explanation:
GRANT ROLE to ROLE/USER
Incorrect Answer: ARole can be grant to user CCreate table privilege is not granted DExecute privilege is not granted FDelete privilege is not granted
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 13-15
NEW QUESTION 4
Which two statements are true regarding single row functions? (Choose two.)
- A. They can be nested only to two levels
- B. They always return a single result row for every row of a queried table
- C. Arguments can only be column values or constant
- D. They can return a data type value different from the one that is referenced
- E. They accept only a single argument
Answer: BD
Explanation:
A function is a program written to optionally accept input parameters, perform an operation, or return a single value. A function returns only one value per execution. Three important components form the basis of defining a function. The first is the input parameter list. It specifies zero or more arguments that may be passed to a function as input for processing. These arguments or parameters may be of differing data types, and some are mandatory while others may be optional. The second component is the data type of its resultant value. Upon execution, only one value is returned by the function. The third encapsulates the details of the processing performed by the function and contains the program code that optionally manipulates the input parameters, performs calculations and operations, and generates a return value.
NEW QUESTION 5
What is true about the WITH GRANT OPTION clause?
- A. It allows a grantee DBA privilege
- B. It is required syntax for object privilege
- C. It allows privileges on specified columns of table
- D. It is used to grant an object privilege on a foreign key colum
- E. It allows the grantee to grant object privileges to other users and role
Answer: AE
Explanation: The GRANT command with the WITH GRANT OPTION clause allows the grantee to grant
object privileges to other users and roles.
Incorrect Answers
A:The WITH GRANT OPTION does not allow a grantee DBA privileges.
B:It is not required syntax for object privileges. It is optional clause of GRANT command.
C:GRANT command does not allows privileges on columns of tables.
D:It is not used to grant an object privilege on a foreign key column.
OCP Introduction to Oracle 9i: SQL Exam Guide, Jason Couchman, p. 356-365
Chapter 8: User Access in Oracle
NEW QUESTION 6
The STUDENT_GRADES table has these columns: 
Which statement finds students who have a grade point average (GPA) greater than 3.0 for the calendar year 2001?
- A. SELECT student_id, gpa FROM student_grades WHERE semester_end BETWEEN ’01-JAN-2001’ AND ’31-DEC-2001’ OR gpa > 3.;
- B. SELECT student_id, gpa FROM student_grades WHERE semester_end BETWEEN ’01-JAN-2001’ AND ’31-DEC-2001’ AND gpa gt 3.0;
- C. SELECT student_id, gpa FROM student_grades WHERE semester_end BETWEEN ’01-JAN-2001’ AND ’31-DEC-2001’ AND gpa > 3.0;
- D. SELECT student_id, gpa FROM student_grades WHERE semester_end BETWEEN ’01-JAN-2001’ AND ’31-DEC-2001’ OR gpa > 3.0;
- E. SELECT student_id, gpa FROM student_grades WHERE semester_end > ’01-JAN-2001’ OR semester_end < ’31-DEC-2001’ AND gpa >= 3.0;
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 7
Evaluate the following SQL statement:
Which statement is true regarding the outcome of the above query?
- A. It produces an error because the ORDER BY clause should appear only at the end of a compound query-that is, with the last SELECT statement
- B. It executes successfully and displays rows in the descending order of PROMO_CATEGORY
- C. It executes successfully but ignores the ORDER BY clause because it is not located at the end of the compound statement
- D. It produces an error because positional notation cannot be used in the ORDER BY clause with SET operators
Answer: A
Explanation:
Using the ORDER BY Clause in Set Operations
The ORDER BY clause can appear only once at the end of the compound query.
Component queries cannot have individual ORDER BY clauses.
The ORDER BY clause recognizes only the columns of the first SELECT query.
By default, the first column of the first SELECT query is used to sort the output in an
ascending order.
NEW QUESTION 8
Examine the description of the EMP_DETAILS table given below: Exhibit: 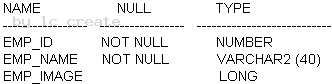
Which two statements are true regarding SQL statements that can be executed on the EMP_DETAIL table? (Choose two.)
- A. An EMP_IMAGE column can be included in the GROUP BY clause
- B. You cannot add a new column to the table with LONG as the data type
- C. An EMP_IMAGE column cannot be included in the ORDER BY clause
- D. You can alter the table to include the NOT NULL constraint on the EMP_IMAGE column
Answer: BC
Explanation:
LONG Character data in the database character set, up to 2GB. All the functionality of LONG (and more) is provided by CLOB; LONGs should not be used in a modern database, and if your database has any columns of this type they should be converted to CLOB.
There can only be one LONG column in a table.
Guidelines
A LONG column is not copied when a table is created using a subquery.
A LONG column cannot be included in a GROUP BY or an ORDER BY clause.
Only one LONG column can be used per table.
No constraints can be defined on a LONG column.
You might want to use a CLOB column rather than a LONG column.
NEW QUESTION 9
Examine the structure of the EMPLOYEES and NEW_EMPLOYEES tables: 
Which DELETE statement is valid?
- A. DELETE FROM employeesWHERE employee_id = (SELECT employee_id FROM employees);
- B. DELETE * FROM employeesWHERE employee_id=(SELECT employee_id FROM new_employees);
- C. DELETE FROM employeesWHERE employee_id IN (SELECT employee_id FROM new_employees WHERE name = ‘Carrey’);
- D. DELETE * FROM employeesWHERE employee_id IN (SELECT employee_id FROM new_employees WHERE name = ‘Carrey’);
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 10
You need to calculate the number of days from 1st January 2007 till date . Dates are stored in the default format of dd-mon-rr. Which two SQL statements would give the required output? (Choose two.)
- A. SELECT SYSDATE - '01-JAN-2007' FROM DUAL:
- B. SELECT SYSDATE - TOJDATE(X)1/JANUARY/2007") FROM DUAL:
- C. SELECT SYSDATE - TOJDATE('01-JANUARY-2007') FROM DUAL:
- D. SELECT TO_CHAR(SYSDAT
- E. 'DD-MON-YYYY') - '01-JAN-2007' FROM DUAL:
- F. SELECT TO_DATE(SYSDAT
- G. *DD/MONTH/YYYY') - '01/JANUARY/2007' FROM DUAL:
Answer: BC
NEW QUESTION 11
See the Exhibit and examine the structure of the SALES, CUSTOMERS, PRODUCTS and ITEMS tables: 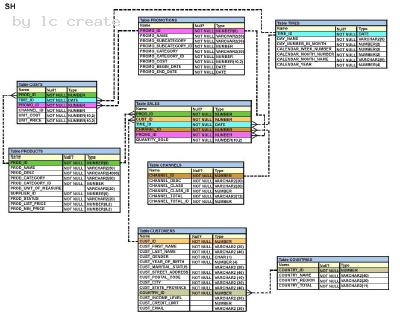
The PROD_ID column is the foreign key in the SALES table, which references the PRODUCTS table. Similarly, the CUST_ID and TIME_ID columns are also foreign keys in the SALES table referencing the CUSTOMERS and TIMES tables, respectively.
Evaluate the following the CREATE TABLE command:
Exhibit:
Which statement is true regarding the above command?
- A. The NEW_SALES table would not get created because the column names in the CREATE TABLE command and the SELECT clause do not match
- B. The NEW_SALES table would get created and all the NOT NULL constraints defined on the specified columns would be passed to the new table
- C. The NEW_SALES table would not get created because the DEFAULT value cannot be specified in the column definition
- D. The NEW_SALES table would get created and all the FOREIGN KEY constraints defined on the specified columns would be passed to the new table
Answer: B
Explanation:
Creating a Table Using a Subquery
Create a table and insert rows by combining the CREATE
TABLE statement and the AS subquery option.
CREATE TABLE table
[(column, column...)]
AS subquery;
Match the number of specified columns to the number of subquery columns.
Define columns with column names and default values.
Guidelines
The table is created with the specified column names, and the rows retrieved by the
SELECT statement are inserted into the table.
The column definition can contain only the column name and default value.
If column specifications are given, the number of columns must equal the number of
columns in the subquery SELECT list.
If no column specifications are given, the column names of the table are the same as the
column names in the subquery.
The column data type definitions and the NOT NULL constraint are passed to the new
table. Note that only the explicit NOT NULL constraint will be inherited. The PRIMARY KEY
column will not pass the NOT NULL feature to the new column. Any other constraint rules
are not passed to the new table. However, you can add constraints in the column definition.
NEW QUESTION 12
You need to display the first names of all customers from the CUSTOMERS table that contain the character 'e' and have the character 'a' in the second last position.
Which query would give the required output?
- A. SELECT cust_first_name FROM customers WHERE INSTR(cust_first_name, 'e')<>0 AND SUBSTR(cust_first_name, -2, 1)='a';
- B. SELECT cust_first_name FROM customers WHERE INSTR(cust_first_name, 'e')<>'' AND SUBSTR(cust_first_name, -2, 1)='a';
- C. SELECT cust_first_name FROM customers WHERE INSTR(cust_first_name, 'e')IS NOT NULL AND SUBSTR(cust_first_name, 1,-2)='a';
- D. SELECT cust_first_name FROM customers WHERE INSTR(cust_first_name, 'e')<>0 AND SUBSTR(cust_first_name, LENGTH(cust_first_name),-2)='a';
Answer: A
Explanation:
The SUBSTR(string, start position, number of characters) function accepts three
parameters and returns a string consisting of the number of characters extracted from the
source string, beginning at the specified start position:
substr('http://www.domain.com',12,6) = domain
The position at which the first character of the returned string begins.
When position is 0 (zero), then it is treated as 1.
When position is positive, then the function counts from the beginning of string to find the
first character.
When position is negative, then the function counts backward from the end of string.
substring_length
The length of the returned string. SUBSTR calculates lengths using characters as defined
by the input character set. SUBSTRB uses bytes instead of characters. SUBSTRC uses
Unicode complete characters.
SUBSTR2 uses UCS2 code points. SUBSTR4 uses UCS4 code points.
When you do not specify a value for this argument, then the function
The INSTR(source string, search item, [start position],[nth occurrence of search item])
function returns a number that represents the position in the source string, beginning from
the given start position, where the nth occurrence of the search item begins:
instr('http://www.domain.com','.',1,2) = 18
NEW QUESTION 13
Examine the structure of the EMP_DEPT_VU view: 
Which SQL statement produces an error?
- A. SELECT * FROM emp_dept_vu;
- B. SELECT department_id, SUM(salary) FROM emp_dept_vu GROUP BY department_id;
- C. SELECT department_id, job_id, AVG(salary) FROM emp_dept_vu GROUP BY department_id, job_id;
- D. SELECT job_id, SUM(salary) FROM emp_dept_vu WHERE department_id IN (10,20) GROUP BY job_id HAVING SUM(salary) > 20000;
- E. None of the statements produce an error; all are vali
Answer: E
Explanation: Explanation: None of the statements produce an error. Incorrect Answer: AStatement will not cause error BStatement will not cause error CStatement will not cause error DStatement will not cause error
NEW QUESTION 14
Which three statements are true regarding subqueries? (Choose three.)
- A. Subqueries can contain GROUP BY and ORDER BY clause
- B. Main query and subquery can get data from different table
- C. Main query and subquery must get data from the same table
- D. Subqueries can contain ORDER BY but not the GROUP BY claus
- E. Only one column or expression can be compared between the main query and subquer
- F. Multiple columns or expressions can be compared between the main query and subquer
Answer: ABF
Explanation:
SUBQUERIES can be used in the SELECT list and in the FROM, WHERE, and HAVING
clauses of a query.
A subquery can have any of the usual clauses for selection and projection. The following
are required clauses:
A SELECT list
A FROM clause
The following are optional clauses: WHERE GROUP BY HAVING
The subquery (or subqueries) within a statement must be executed before the parent query that calls it, in order that the results of the subquery can be passed to the parent.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which three SQL statements would display the value 1890.55 as $1,890.55? (Choose three.)
- A. SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$99G999D00') FROM DUAL;
- B. SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$9,999V99') FROM DUAL;
- C. SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$0G000D00') FROM DUAL;
- D. SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$99G999D99') FROM DUAL;
- E. SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$9,999D99') FROM DUAL;
Answer: ACD
NEW QUESTION 16
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of CUSTOMERS table. Evaluate the following query: 
Which statement is true regarding the above query? 
- A. It executes successfull
- B. It produces an error because the condition on the CUST_CITY column is not vali
- C. It produces an error because the condition on the CUST_FIRST_NAME column is not vali
- D. It produces an error because conditions on the CUST_CREDIT_LIMIT column are not vali
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 17
Which two statements are true regarding tables? (Choose two.)
- A. A table name can be of any lengt
- B. A table can have any number of column
- C. A column that has a DEFAULT value cannot store null value
- D. A table and a view can have the same name in the same schem
- E. A table and a synonym can have the same name in the same schem
- F. The same table name can be used in different schemas in the same databas
Answer: EF
Explanation:
Synonyms Synonyms are database objects that enable you to call a table by another name. You can create synonyms to give an alternative name to a table.
NEW QUESTION 18
Examine the structure of the EMPLOYEES and NEW_EMPLOYEES tables: 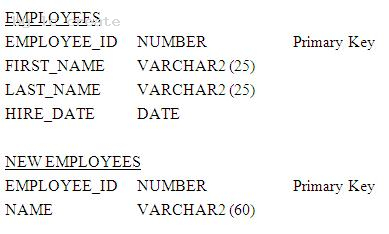
Which DELETE statement is valid?
- A. DELETE FROM employees WHERE employee_id = (SELECT employee_id FROM employees);
- B. DELETE * FROM employees WHERE employee_id = (SELECT employee_id FROM new_employees);
- C. DELETE FROM employees WHERE employee_id IN(SELECT employee_id FROM new_employees WHERE name = 'Carrey');
- D. DELETE * FROM employees WHERE employee_id IN (SELECT employee_id FROM new_employees WHERE last_name = 'Carrey');
Answer: C
Explanation:
The correct syntax for DELETE statement
DELETE [ FROM ] table
[ WHERE condition ];
Incorrect Answers :
A. '=' is use in the statement and sub query will return more than one row.
Error Ora-01427: single-row sub query returns more than one row.
B. Incorrect DELETE statement
D. Incorrect DELETE statement
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Student Guide, Manipulating Data,
p. 8-19
NEW QUESTION 19
Examine the structure of the TRANSACTIONS table:
Name Null Type
TRANS_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(3)
CUST_NAME VARCHAR2(30) TRANS_DATE DATE TRANS_AMT NUMBER(10,2)
You want to display the transaction date and specify whether it is a weekday or weekend. Evaluate the following two queries: 
Which statement is true regarding the above queries?
- A. Both give wrong result
- B. Both give the correct resul
- C. Only the first query gives the correct resul
- D. Only the second query gives the correct resul
Answer: C
Explanation:
Range Conditions Using the BETWEEN Operator Use the BETWEEN operator to display rows based on a range of values: SELECT last_name, salary FROM employees WHERE salary BETWEEN 2500 AND 3500; Range Conditions Using the BETWEEN Operator You can display rows based on a range of values using the BETWEEN operator. The range that you specify contains a lower limit and an upper limit. The SELECT statement in the slide returns rows from the EMPLOYEES table for any employee whose salary is between $2,500 and $3,500. Values that are specified with the BETWEEN operator are inclusive. However, you must specify the lower limit first. You can also use the BETWEEN operator on character values: SELECT last_name FROM employees WHERE last_name BETWEEN 'King' AND 'Smith';
100% Valid and Newest Version 1Z0-051 Questions & Answers shared by Surepassexam, Get Full Dumps HERE: https://www.surepassexam.com/1Z0-051-exam-dumps.html (New 292 Q&As)
- Download Oracle 1Z0-819 Actual Test Online
- All About Precise 1z0-1046-20 Free Practice Questions
- Simulation Oracle 1Z0-447 dumps
- Oracle 1z0-1052 Guidance 2021
- How Many Questions Of 1z0-976 Free Practice Questions
- Precise 1Z0-051 Dumps 2021
- Oracle 1Z0-063 Dumps 2021
- Oracle 1Z0-053 Dumps Questions 2021
- Updated 1z0-1064 Free Samples 2021
- Oracle 1Z0-053 Dumps 2021


